Predictive value of von Willebrand factor for venous thrombosis in patients with chronic heart failure complicated with atrial fibrillation after anticoagulant therapy
- PMID: 37442989
- PMCID: PMC10347722
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03167-1
Predictive value of von Willebrand factor for venous thrombosis in patients with chronic heart failure complicated with atrial fibrillation after anticoagulant therapy
Abstract
Background: We investigated the value of von Willebrand factor (vWF) in predicting venous thrombosis in patients with chronic heart failure complicated with atrial fibrillation after anticoagulation therapy.
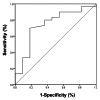
Methods: Totally, 126 patients with chronic heart failure complicated with atrial fibrillation who were treated with anticoagulant therapy and 60 healthy individuals were enrolled. One year after anticoagulant therapy, venous thrombosis occurred in 19 patients. Clinical data of patients were collected. The plasma vWF activity was detected and compared. The logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the influencing factors of vWF. ROC curve was used to evaluate the predictive value of plasma vWF.
Results: Plasma vWF activity was significantly higher in patients with heart failure and atrial fibrillation than control subjects (P < 0.01). The vWF activity in patients with venous thrombosis was significantly higher than that in patients without venous thrombosis (P < 0.01). ROC curve analysis showed that the cut-off value of vWF activity for venous thrombosis within one year after anticoagulant therapy was 267.5%, and the AUC was 0.742 (95% CI: 0.764-0.921, P < 0.05). The sensitivity was 80.0%, and the specificity was 63.6%. Factors of diabetes, myocardial ischemia, old myocardial infarction, and lower extremity atherosclerosis, but not sex, age, coronary heart disease, hypertension, and cardiac function, had significant effect on vWF activity (P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that vWF activity was significantly related with atherosclerosis of lower limbs and old myocardial infarction, but not significantly related with diabetes and myocardial ischemia. The risk of venous thrombosis in patients with vWF activity greater than 267.5% was 10.667 times higher than that in patients with vWF activity less than 267.5% (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The vWF activity greater than 267.5% has clinical predictive value for the risk of lower extremity venous thrombosis in patients with chronic heart failure complicated with atrial fibrillation within 1 year of anticoagulant therapy.
Keywords: Anticoagulant therapy; Atrial fibrillation; Chronic heart failure; Venous thrombosis; Von Willebrand factor.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Anticoagulation status and adherence in patients with atrial fibrillation hospitalized for ACS and the impact on 1-year prognosis: a multicenter cohort study].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2023 Jul 24;51(7):731-741. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20230314-00138. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37460427 Chinese.
-
Plasma von Willebrand factor levels are an independent risk factor for adverse events including mortality and major bleeding in anticoagulated atrial fibrillation patients.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Jun 21;57(25):2496-504. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.12.033. Epub 2011 Apr 14. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21497043
-
Von Willebrand factor is associated with atrial fibrillation development in ischaemic patients after cardiac surgery.Europace. 2016 Sep;18(9):1328-34. doi: 10.1093/europace/euv354. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Europace. 2016. PMID: 26566941
-
Prognostic value of von Willebrand factor in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(27):e11269. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011269. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29979393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticoagulant management by low-dose of low molecular weight heparin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation following hemorrhagic transformation and complicated with venous thrombosis: Five case reports and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Feb 19;100(7):e24189. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024189. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33607764 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pang Z, Yao Z, Tian L, Pan C. A comparative study on the efficacy of rivaroxaban and warfarin in patients with heart failure and atrial fibrillation aged > 75 years. Chin J Geriatric Heart Brain Vessel Dis. 2018;20(11):1153–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2018.11.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous