BID expression determines the apoptotic fate of cancer cells after abrogation of the spindle assembly checkpoint by AURKB or TTK inhibitors
- PMID: 37443114
- PMCID: PMC10339641
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01815-w
BID expression determines the apoptotic fate of cancer cells after abrogation of the spindle assembly checkpoint by AURKB or TTK inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Drugs targeting the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), such as inhibitors of Aurora kinase B (AURKB) and dual specific protein kinase TTK, are in different stages of clinical development. However, cell response to SAC abrogation is poorly understood and there are no markers for patient selection.
Methods: A panel of 53 tumor cell lines of different origins was used. The effects of drugs were analyzed by MTT and flow cytometry. Copy number status was determined by FISH and Q-PCR; mRNA expression by nCounter and RT-Q-PCR and protein expression by Western blotting. CRISPR-Cas9 technology was used for gene knock-out (KO) and a doxycycline-inducible pTRIPZ vector for ectopic expression. Finally, in vivo experiments were performed by implanting cultured cells or fragments of tumors into immunodeficient mice.
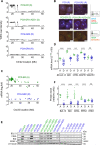
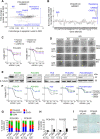
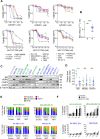
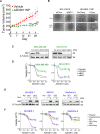
Results: Tumor cells and patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) sensitive to AURKB and TTK inhibitors consistently showed high expression levels of BH3-interacting domain death agonist (BID), while cell lines and PDXs with low BID were uniformly resistant. Gene silencing rendered BID-overexpressing cells insensitive to SAC abrogation while ectopic BID expression in BID-low cells significantly increased sensitivity. SAC abrogation induced activation of CASP-2, leading to cleavage of CASP-3 and extensive cell death only in presence of high levels of BID. Finally, a prevalence study revealed high BID mRNA in 6% of human solid tumors.
Conclusions: The fate of tumor cells after SAC abrogation is driven by an AURKB/ CASP-2 signaling mechanism, regulated by BID levels. Our results pave the way to clinically explore SAC-targeting drugs in tumors with high BID expression.
Keywords: AURKB inhibitor; Abrogation; BID; Biomarker; CASP-2; Cell cycle; Spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC); TTK inhibitor; Tumor.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
I.S. has received fees for consultancy or advisory roles from Roche, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim and Takeda. N.R. has received fees for consultancy or advisory roles from Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. A.A.H. has received fees for consultancy or advisory roles from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp and Lilly. J.T., S.T., R.W., N.F., G.G., M.X., P.S., J.S., G.F., A.G., U.P. and J.U. are current or former AstraZeneca employees and shareholders. M.A.M.V. has received research funding from Astra Zeneca, In3Bio and Merck Healthcare KGaA. The rest of the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Age-dependent integrity of the meiotic spindle assembly checkpoint in females requires Aurora kinase B.Aging Cell. 2021 Nov;20(11):e13489. doi: 10.1111/acel.13489. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Aging Cell. 2021. PMID: 34704342 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora B phosphorylates Bub1 to promote spindle assembly checkpoint signaling.Curr Biol. 2022 Jan 10;32(1):237-247.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.10.049. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 34861183 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome duplication increases tumor cell sensitivity to MPS1 inhibition.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 5;7(1):885-901. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6432. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26637805 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic syndicates Aurora Kinase B (AURKB) and mitotic arrest deficient 2 like 2 (MAD2L2) in cohorts of DNA damage response (DDR) and tumorigenesis.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021 Jan-Jun;787:108376. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2021.108376. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2021. PMID: 34083040 Review.
-
Aurora Kinase B Inhibition: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer.Molecules. 2021 Apr 1;26(7):1981. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071981. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33915740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA938/ TAF9/TTK axis promotes EMT and serves as a therapeutic target in hepatoblastoma.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 21;23(1):946. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06809-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40841910 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling BID: a key biomarker in apoptosis post-intracerebral hemorrhage.Front Neurol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1533558. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1533558. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40093739 Free PMC article.
-
A new era in cancer therapy: targeting the Proteasome-Bcl-2 axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 21;44(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03505-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40841912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aurora B inhibition induces hyper-polyploidy and loss of long-term proliferative potential in RB and p53 defective cells.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):7. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07329-7. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 39779678 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms within autophagy-related genes as susceptibility biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of three large European cohorts and functional characterization.Int J Cancer. 2025 Jan 15;156(2):339-352. doi: 10.1002/ijc.35196. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Int J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39319538 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

