Region of interest (ROI) selection using vision transformer for automatic analysis using whole slide images
- PMID: 37443188
- PMCID: PMC10344922
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38109-6
Region of interest (ROI) selection using vision transformer for automatic analysis using whole slide images
Abstract
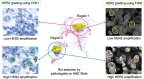
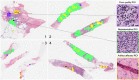
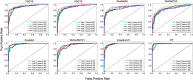
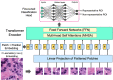
Selecting regions of interest (ROI) is a common step in medical image analysis across all imaging modalities. An ROI is a subset of an image appropriate for the intended analysis and identified manually by experts. In modern pathology, the analysis involves processing multidimensional and high resolution whole slide image (WSI) tiles automatically with an overwhelming quantity of structural and functional information. Despite recent improvements in computing capacity, analyzing such a plethora of data is challenging but vital to accurate analysis. Automatic ROI detection can significantly reduce the number of pixels to be processed, speed the analysis, improve accuracy and reduce dependency on pathologists. In this paper, we present an ROI detection method for WSI and demonstrated it for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) grading for breast cancer patients. Existing HER2 grading relies on manual ROI selection, which is tedious, time-consuming and suffers from inter-observer and intra-observer variability. This study found that the HER2 grade changes with ROI selection. We proposed an ROI detection method using Vision Transformer and investigated the role of image magnification for ROI detection. This method yielded an accuracy of 99% using 20 × WSI and 97% using 10 × WSI for the ROI detection. In the demonstration, the proposed method increased the diagnostic agreement to 99.3% with the clinical scores and reduced the time to 15 seconds for automated HER2 grading.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Hossain, M. S. et al.. Tissue artifact segmentation and severity assessment for automatic analysis using wsi. IEEE Access (2023).
-
- Caccomo S. Fda Allows Marketing of First Whole Slide Imaging System for Digital Pathology. US Department of Health and Human Services; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

