Association between levothyroxine treatment for maternal subclinical hypothyroidism with negative TPOAb and early child neurodevelopment: A prospective real-world clinical trial
- PMID: 37443452
- PMCID: PMC10407020
- DOI: 10.1111/aogs.14602
Association between levothyroxine treatment for maternal subclinical hypothyroidism with negative TPOAb and early child neurodevelopment: A prospective real-world clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) during pregnancy is reported to have detrimental impact on pregnancy and child development. However, its treatment indications require further investigation in different thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) status.
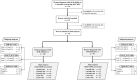
Material and methods: This was a secondary analysis of a Chinese prospective cohort in a real-world setting. Pregnant women with gestational SCH were enrolled at the first antenatal visit and grouped by TPOAb positivity. Child neurodevelopment was assessed by the Gesell development diagnosis scale (GDDS) at one, three, six, 12, and 24 months of age. Subgroup analyses and sensitivity analyses were also conducted.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01744743.
Results: From January 2012 to December 2013, a total of 171 participants were enrolled, including 116 of SCH with TPOAb negative (SCH-TPOAb [-]) and 55 of SCH with TPOAb positive (SCH-TPOAb [+]). Compared to women in the SCH-TPOAb (+) group, those in the SCH-TPOAb (-) group had lower thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels at enrollment and 12-16+6 gestational weeks, and unexpectedly higher TSH levels at 30-34+6 gestational weeks and delivery, with a correspondingly lower levothyroxine dosage throughout pregnancy (all p < 0.05). Offspring in the SCH-TPOAb (-) group displayed lower GDDS scores at one year old than did their counterparts (adjusted p < 0.05), which was possibly related to the worse thyroid function control of maternal SCH-TPOAb (-). No statistically significant difference was found in the GDDS assessments of children at one, three, six, and 24 months of age. These results were also confirmed in subgroup analyses stratified by maternal thyroid characteristics at enrollment, namely TSH levels, free levothyroxine (T4 ) levels, and anti-thyroglobulin antibody (TgAb) status, as well as in sensitivity analyses excluding participants with no levothyroxine treatment at enrollment.
Conclusions: In the current clinical practice, infants born to mothers with SCH-TPOAb (-) displayed slightly lower neurodevelopmental scores at one year old than did those born to mothers with SCH-TPOAb (+) but this difference was not seen at two years.
Keywords: Gesell development diagnosis scale; child neurodevelopment; levothyroxine; pregnancy; subclinical hypothyroidism; thyroid peroxidase antibody.
© 2023 The Authors. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology (NFOG).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Teng W, Shan Z, Patil‐Sisodia K, Cooper DS. Hypothyroidism in pregnancy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013;1:228‐237. - PubMed
-
- Alexander EK, Pearce EN, Brent GA, et al. 2017 guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and the postpartum. Thyroid. 2017;27:315‐389. - PubMed
-
- Ad Hoc Writing Committee for Guidelines on Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy and Postpartum, Chinese Society of Endocrinology of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Perinatology of Chinese Medical Association . Guideline on diagnosis and management of thyroid diseases during pregnancy and postpartum (2nd edition). Chin J Endocrinol Metab. 2019;35:636‐665. [article in Chinese].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

