Predicting the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Using Deep Learning of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Videos
- PMID: 37443577
- PMCID: PMC10341263
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13132183
Predicting the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Using Deep Learning of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Videos
Abstract
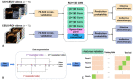
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) is a promising imaging modality in predicting the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer, a tumor with high mortality. In this study, we proposed a deep-learning-based strategy for analyzing CEUS videos to predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN) models were used for binary classification of the chemotherapy as effective or ineffective, with CEUS videos collected before chemotherapy as the model input, and with the efficacy after chemotherapy as the reference standard. We proposed two deep learning models. The first CNN model used videos of ultrasound (US) and CEUS (US+CEUS), while the second CNN model only used videos of selected regions of interest (ROIs) within CEUS (CEUS-ROI). A total of 38 patients with strict restriction of clinical factors were enrolled, with 76 original CEUS videos collected. After data augmentation, 760 and 720 videos were included for the two CNN models, respectively. Seventy-six-fold and 72-fold cross-validations were performed to validate the classification performance of the two CNN models. The areas under the curve were 0.892 and 0.908 for the two models. The accuracy, recall, precision and F1 score were 0.829, 0.759, 0.786, and 0.772 for the first model. Those were 0.864, 0.930, 0.866, and 0.897 for the second model. A total of 38.2% and 40.3% of the original videos could be clearly distinguished by the deep learning models when the naked eye made an inaccurate classification. This study is the first to demonstrate the feasibility and potential of deep learning models based on pre-chemotherapy CEUS videos in predicting the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for pancreas cancer.
Keywords: contrast-enhanced ultrasound; deep learning; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; pancreatic cancer; prognosis prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Tawada K., Yamaguchi T., Kobayashi A., Ishihara T., Sudo K., Nakamura K., Hara T., Denda T., Matsuyama M., Yokosuka O. Changes in tumor vascularity depicted by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography as a predictor of chemotherapeutic effect in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 2009;38:30–35. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318183ff73. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sidhu P.S., Cantisani V., Dietrich C.F., Gilja O.H., Saftoiu A., Bartels E., Bertolotto M., Calliada F., Clevert D.A., Cosgrove D., et al. The EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations for the clinical practice of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in non-hepatic applications: Update 2017 (Short Version) Ultraschall Med. 2018;39:154–180. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 82171968/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81873902/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020-I2M-C&T-B-039/Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2022-PUMCH-B-065/National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding
- 2022-PUMCH-D-001/National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

