Multimodal Spatiotemporal Deep Learning Framework to Predict Response of Breast Cancer to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy
- PMID: 37443648
- PMCID: PMC10340375
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13132251
Multimodal Spatiotemporal Deep Learning Framework to Predict Response of Breast Cancer to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy
Abstract
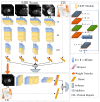
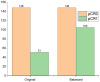
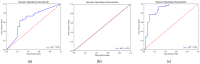
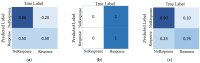
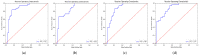
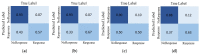
Current approaches to breast cancer therapy include neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NST). The efficacy of NST is measured by pathologic complete response (pCR). A patient who attains pCR has significantly enhanced disease-free survival progress. The accurate prediction of pCR in response to a given treatment regimen could increase the likelihood of achieving pCR and prevent toxicities caused by treatments that are not effective. Th early prediction of response to NST can increase the likelihood of survival and help with decisions regarding breast-conserving surgery. An automated NST prediction framework that is able to precisely predict which patient undergoing NST will achieve a pathological complete response (pCR) at an early stage of treatment is needed. Here, we propose an end-to-end efficient multimodal spatiotemporal deep learning framework (deep-NST) framework to predict the outcome of NST prior or at an early stage of treatment. The deep-NST model incorporates imaging data captured at different timestamps of NST regimens, a tumor's molecular data, and a patient's demographic data. The efficacy of the proposed work is validated on the publicly available ISPY-1 dataset, in terms of accuracy, area under the curve (AUC), and computational complexity. In addition, seven ablation experiments were carried out to evaluate the impact of each design module in the proposed work. The experimental results show that the proposed framework performs significantly better than other recent methods.
Keywords: 3D-CNN multimodal framework; automated neoadjuvant systematic therapy prediction; multimodal deep learning framework.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of neoadjuvant therapy on eligibility for and frequency of breast conservation in stage II-III HER2-positive breast cancer: surgical results of CALGB 40601 (Alliance).Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Nov;160(2):297-304. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-4006-6. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27704226 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying pathologic complete response of the breast after neoadjuvant systemic therapy with ultrasound guided biopsy to eventually omit surgery: Study design and feasibility of the MICRA trial (Minimally Invasive Complete Response Assessment).Breast. 2018 Aug;40:76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2018.04.015. Epub 2018 May 22. Breast. 2018. PMID: 29698928
-
A novel nomogram containing efficacy indicators to predict axillary pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant systemic therapy in breast cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 25;13:1042394. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1042394. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36506067 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative Standards in Surgery of the Breast after Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy.Breast Care (Basel). 2021 Dec;16(6):590-597. doi: 10.1159/000520051. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Breast Care (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35087362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
Cited by
-
Multimodal deep learning for predicting neoadjuvant treatment outcomes in breast cancer: a systematic review.Biol Direct. 2025 Jun 23;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13062-025-00661-8. Biol Direct. 2025. PMID: 40551237 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning model for the early prediction of pathologic response following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 25;15:1491843. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1491843. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40071096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braman N.M., Etesami M., Prasanna P., Dubchuk C., Gilmore H., Tiwari P., Plecha D., Madabhushi A. Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for the pretreatment prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on breast DCE-MRI. Breast Cancer Res. 2017;19:1–14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hylton N.M., Blume J.D., Bernreuter W.K., Pisano E.D., Rosen M.A., Morris E.A., Weatherall P.T., Lehman C.D., Newstead G.M., Polin S., et al. Locally advanced breast cancer: MR imaging for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy—Results from ACRIN 6657/I-SPY TRIAL. Radiology. 2012;263:663–672. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12110748. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hylton N.M., Gatsonis C.A., Rosen M.A., Lehman C.D., Newitt D.C., Partridge S.C., Bernreuter W.K., Pisano E.D., Morris E.A., Weatherall P.T., et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: Functional tumor volume by MR imaging predicts recurrence-free survival—Results from the ACRIN 6657/CALGB 150007 I-SPY 1 TRIAL. Radiology. 2016;279:44–55. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

