The Predictive Value of Lung Ultrasound Score on Hemodynamically Significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus among Neonates ≤25 Weeks
- PMID: 37443657
- PMCID: PMC10341262
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13132263
The Predictive Value of Lung Ultrasound Score on Hemodynamically Significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus among Neonates ≤25 Weeks
Abstract
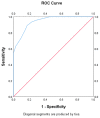
Lung ultrasound (LU) is increasingly used to diagnose and monitor neonatal pulmonary disorders; however, its role in hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus (hsPDA) has not been elucidated. This prospective study investigated the predictive value of the LU score (LUS) for hsPDA in preterm infants with gestational age (GA) ≤ 25 weeks. Preterm infants with GA ≤ 25 weeks were enrolled in this study. LU was conducted on the fourth day of life (DOL). Six lung regions in every lung were scanned, with each region rated as 0-4 points. The performance of the LUS in predicting hsPDA among infants aged ≤25 weeks was analyzed by plotting the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. A total of 81 infants were included in this study. GA, birth weight (BW), gender, Apgar score, delivery mode, antenatal steroids, meconium-stained amniotic fluid, premature rapture of membrane, and early-onset sepsis were not significantly different, but infants in the hsPDA group had increased LUS (38.2 ± 2.8 vs. 30.3 ± 4.3, p < 0.001) compared with non-hsPDA group. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) value of the LUS on the fourth DOL was 0.94 (95% CI: 0.93-0.99) in predicting hsPDA. The LUS threshold at 33 achieved 89% sensitivity and 83% specificity, with the positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV) being 87 and 86%, respectively. The LUS can predict hsPDA in extremely preterm infants at an early stage.
Keywords: lung ultrasound; neonate; patent ductus arteriosus; preterm infant; score.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

