The DTX Protein Family: An Emerging Set of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Cancer
- PMID: 37443713
- PMCID: PMC10340142
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12131680
The DTX Protein Family: An Emerging Set of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Cancer
Abstract
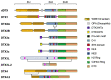
Until recently, Deltex (DTX) proteins have been considered putative E3 ligases, based on the presence of an E3 RING domain in their protein coding sequence. The human DTX family includes DTX1, DTX2, DTX3, DTX3L and DTX4. Despite the fact that our knowledge of this class of E3-ubiquitin ligases is still at an early stage, our understanding of their role in oncogenesis is beginning to unfold. In fact, recently published studies allow us to define specific biological scenarios and further consolidate evidence-based working hypotheses. According to the current evidence, all DTX family members are involved in the regulation of Notch signaling, suggesting a phylogenetically conserved role in the regulation of this pathway. Indeed, additional evidence reveals a wider involvement of these proteins in other signaling complexes and cancer-promoting mechanisms beyond NOTCH signaling. DTX3, in particular, had been known to express two isoform variants (DTX3a and DTX3b). The recent identification and cloning of a third isoform variant in cancer (DTX3c), and its specific involvement in EphB4 degradation in cancer cells, sheds further light on this group of proteins and their specific role in cancer. Herein, we review the cumulative knowledge of this family of E3 Ubiquitin ligases with a specific focus on the potential oncogenic role of DTX isoforms in light of the rapidly expanding findings regarding this protein family's cellular targets and regulated signaling pathways. Furthermore, using a comparative and bioinformatic approach, we here disclose a new putative motif of a member of this family which may help in understanding the biological and contextual differences between the members of these proteins.
Keywords: DTC, Deltex C-terminal (region); Degron; Deltex, DTX; H2-RING, synonym of C3H2C3-RING; HC-RING, synonym of C3HC4-RING; RING, really interesting new gene (motifs); RNF, Ring Finger (domain); UbE3L, Ubiquitin E3 Ligase; pDegron, Phospho-Degron; piDegron, Phospho-inhibited Degron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The BAL-binding protein BBAP and related Deltex family members exhibit ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligase activity.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 13;278(24):21930-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301157200. Epub 2003 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12670957
-
Novel Isoform DTX3c Associates with UBE2N-UBA1 and Cdc48/p97 as Part of the EphB4 Degradation Complex Regulated by the Autocrine IGF-II/IRA Signal in Malignant Mesothelioma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 17;24(8):7380. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087380. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108544 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and Molecular Mechanisms of Deltex Family Ubiquitin E3 Ligases in Development and Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 25;9:706997. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.706997. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34513839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitylation of nucleic acids by DELTEX ubiquitin E3 ligase DTX3L.EMBO Rep. 2024 Oct;25(10):4172-4189. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00235-1. Epub 2024 Sep 6. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39242775 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM proteins as RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:27-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5398-7_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23630998 Review.
Cited by
-
p-STAT3-elevated E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX4 confers the stability of HBV cccDNA by ubiquitinating APOBEC3B in liver.Theranostics. 2024 Sep 16;14(15):6036-6052. doi: 10.7150/thno.99407. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39346550 Free PMC article.
-
Deltex and RING-UIM E3 ligases cooperate to create a ubiquitin-ADP-ribose hybrid mark on tankyrase, promoting its stabilization.Sci Adv. 2025 Sep 5;11(36):eadx7172. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adx7172. Epub 2025 Sep 3. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40901936 Free PMC article.
-
The activation of the Notch signaling pathway by UBE2C promotes the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 1;14(1):22859. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72714-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39353974 Free PMC article.
-
Sialyltransferase-related genes as predictive factors for therapeutic response and prognosis in cervical cancer.PeerJ. 2025 May 22;13:e19422. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19422. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40416607 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression by degradation rescue of RTKs via cancer-secreted autocrine growth factors: a Phospho-degron-driven actionable layer of post-translational regulation?.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 26;13:1278402. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1278402. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37823054 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

