Amazonia Phytotherapy Reduces Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in the Kidneys
- PMID: 37443721
- PMCID: PMC10341095
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12131688
Amazonia Phytotherapy Reduces Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in the Kidneys
Abstract
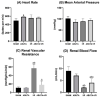
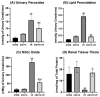
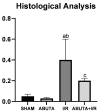
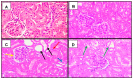
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is defined as a sudden decrease in kidney function. Phytomedicines have shown positive effects in the treatment of AKI worldwide. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of Abuta grandifolia on the renal function of rats submitted to AKI. A phytochemical study of the plant was performed through liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (CL-EM) and DPPH and ABTS antioxidant tests. Renal function tests were performed in 20 male adult Wistar rats weighing from 250 to 300 g distributed in the following groups: SHAM (submitted to laparotomy with simulation of renal ischemia); ABUTA (animals that received 400 mg/kg of AG, orally-VO, once a day, for 5 days, with simulation of renal ischemia); I/N (animals submitted to laparotomy for clamping of bilateral renal pedicles for 30 min, followed by reperfusion); ABUTA + I/R (animals that received AG-400 mg/kg, 1× per day, VO, for 5 days, submitted to renal ischemia after treatment with herbal medicine). The results suggest that the consumption of Abuta grandifolia promoted renoprotection, preventing the reduction of renal function induced by ischemia, oxidizing activity, and deleterious effects on the renal tissue, confirmed by the decrease of oxidative metabolites and increase of antioxidants in the animals' organisms.
Keywords: acute kidney disease; ischemia/reperfusion; phytotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nephroprotective effects of (-)-α-bisabolol against ischemic-reperfusion acute kidney injury.Phytomedicine. 2016 Dec 15;23(14):1843-1852. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27912887
-
Explicit role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in gallic acid-mediated protection against ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in rats.J Surg Res. 2014 Apr;187(2):631-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.11.1088. Epub 2013 Nov 22. J Surg Res. 2014. PMID: 24433871
-
Effect of Otostegia persica extraction on renal injury induced by hindlimb ischemia-reperfusion: a rat model.Int J Surg. 2015 Jan;13:124-130. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.11.047. Epub 2014 Dec 6. Int J Surg. 2015. PMID: 25486262
-
Antioxidant effect of zinc on acute renal failure induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Am J Nephrol. 1999;19(5):609-14. doi: 10.1159/000013529. Am J Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10575193
-
The Effects of Quercetin on Apoptosis and Antioxidant Activity in a Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Animal Model.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2023 Jun;73(5):255-262. doi: 10.1055/a-1999-7600. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2023. PMID: 36972618
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

