Ultrasound Imaging with Flexible Array Transducer for Pancreatic Cancer Radiation Therapy
- PMID: 37444403
- PMCID: PMC10340354
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15133294
Ultrasound Imaging with Flexible Array Transducer for Pancreatic Cancer Radiation Therapy
Abstract
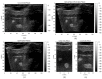
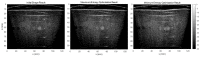
Pancreatic cancer with less than 10% 3-year survival rate is one of deadliest cancer types and greatly benefits from enhanced radiotherapy. Organ motion monitoring helps spare the normal tissue from high radiation and, in turn, enables the dose escalation to the target that has been shown to improve the effectiveness of RT by doubling and tripling post-RT survival rate. The flexible array transducer is a novel and promising solution to address the limitation of conventional US probes. We proposed a novel shape estimation for flexible array transducer using two sequential algorithms: (i) an optical tracking-based system that uses the optical markers coordinates attached to the probe at specific positions to estimate the array shape in real-time and (ii) a fully automatic shape optimization algorithm that automatically searches for the optimal array shape that results in the highest quality reconstructed image. We conducted phantom and in vivo experiments to evaluate the estimated array shapes and the accuracy of reconstructed US images. The proposed method reconstructed US images with low full-width-at-half-maximum (FWHM) of the point scatters, correct aspect ratio of the cyst, and high-matching score with the ground truth. Our results demonstrated that the proposed methods reconstruct high-quality ultrasound images with significantly less defocusing and distortion compared with those without any correction. Specifically, the automatic optimization method reduced the array shape estimation error to less than half-wavelength of transmitted wave, resulting in a high-quality reconstructed image.
Keywords: abdominal motion monitoring; flexible array transducer; gastrointestinal malignancies; pancreatic cancer; ultrasound imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











References
-
- Han-Oh S., Hill C., Kang-Hsin Wang K., Ding K., Wright J.L., Alcorn S., Meyer J., Herman J., Narang A. Geometric Reproducibility of Fiducial Markers and Efficacy of a Patient-Specific Margin Design Using Deep Inspiration Breath Hold for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021;6:100655. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2021.100655. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ting L.-L., Chuang H.-C., Liao A.-H., Kuo C.-C., Yu H.-W., Tsai H.-C., Tien D.-C., Jeng S.-C., Chiou J.-F. Tumor Motion Tracking Based on a Four-Dimensional Computed Tomography Respiratory Motion Model Driven by an Ultrasound Tracking Technique. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020;10:26. doi: 10.21037/qims.2019.09.02. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger A.C., Garcia M., Jr., Hoffman J.P., Regine W.F., Abrams R.A., Safran H., Konski A., Benson A.B., 3rd, MacDonald J., Willett C.G. Postresection CA 19-9 Predicts Overall Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer Treated with Adjuvant Chemoradiation: A Prospective Validation by RTOG 9704. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:5918–5922. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.6288. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

