Al-Biruni Earth Radius Optimization with Transfer Learning Based Histopathological Image Analysis for Lung and Colon Cancer Detection
- PMID: 37444410
- PMCID: PMC10340056
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15133300
Al-Biruni Earth Radius Optimization with Transfer Learning Based Histopathological Image Analysis for Lung and Colon Cancer Detection
Abstract
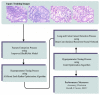
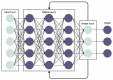
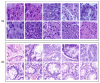
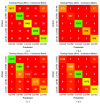
An early diagnosis of lung and colon cancer (LCC) is critical for improved patient outcomes and effective treatment. Histopathological image (HSI) analysis has emerged as a robust tool for cancer diagnosis. HSI analysis for a LCC diagnosis includes the analysis and examination of tissue samples attained from the LCC to recognize lesions or cancerous cells. It has a significant role in the staging and diagnosis of this tumor, which aids in the prognosis and treatment planning, but a manual analysis of the image is subject to human error and is also time-consuming. Therefore, a computer-aided approach is needed for the detection of LCC using HSI. Transfer learning (TL) leverages pretrained deep learning (DL) algorithms that have been trained on a larger dataset for extracting related features from the HIS, which are then used for training a classifier for a tumor diagnosis. This manuscript offers the design of the Al-Biruni Earth Radius Optimization with Transfer Learning-based Histopathological Image Analysis for Lung and Colon Cancer Detection (BERTL-HIALCCD) technique. The purpose of the study is to detect LCC effectually in histopathological images. To execute this, the BERTL-HIALCCD method follows the concepts of computer vision (CV) and transfer learning for accurate LCC detection. When using the BERTL-HIALCCD technique, an improved ShuffleNet model is applied for the feature extraction process, and its hyperparameters are chosen by the BER system. For the effectual recognition of LCC, a deep convolutional recurrent neural network (DCRNN) model is applied. Finally, the coati optimization algorithm (COA) is exploited for the parameter choice of the DCRNN approach. For examining the efficacy of the BERTL-HIALCCD technique, a comprehensive group of experiments was conducted on a large dataset of histopathological images. The experimental outcomes demonstrate that the combination of AER and COA algorithms attain an improved performance in cancer detection over the compared models.
Keywords: computer-aided diagnosis; lung and colon cancer; medical image analysis; parameter optimization; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
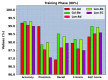
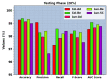
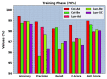
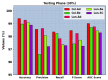
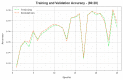
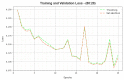
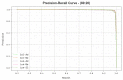
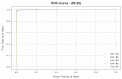
Similar articles
-
Identification of Anomalies in Lung and Colon Cancer Using Computer Vision-Based Swin Transformer with Ensemble Model on Histopathological Images.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;11(10):978. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11100978. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451355 Free PMC article.
-
An Al-Biruni Earth Radius Optimization-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Classifying Monkeypox Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;12(11):2892. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112892. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428952 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting histopathological imaging for early detection of lung and colon cancer via ensemble deep learning model.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 3;14(1):20434. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71302-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39227664 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for colon cancer histopathological images analysis.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Sep;136:104730. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104730. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34375901 Review.
-
Deep Learning in Selected Cancers' Image Analysis-A Survey.J Imaging. 2020 Nov 10;6(11):121. doi: 10.3390/jimaging6110121. J Imaging. 2020. PMID: 34460565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Anomalies in Lung and Colon Cancer Using Computer Vision-Based Swin Transformer with Ensemble Model on Histopathological Images.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;11(10):978. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11100978. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451355 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements and Challenges in the Image-Based Diagnosis of Lung and Colon Cancer: A Comprehensive Review.Cancer Inform. 2024 Oct 16;23:11769351241290608. doi: 10.1177/11769351241290608. eCollection 2024. Cancer Inform. 2024. PMID: 39483315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive analytics of complex healthcare systems using deep learning based disease diagnosis model.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 11;14(1):27497. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78015-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39528485 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic Nuclei Segmentation and Classification Using Chaotic Butterfly Optimization Algorithm with Deep Learning on Histopathology Images.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Oct 5;8(6):474. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8060474. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887605 Free PMC article.
-
Colon and lung cancer classification from multi-modal images using resilient and efficient neural network architectures.Heliyon. 2024 May 3;10(9):e30625. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30625. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38742084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naga Raju M.S., Srinivasa Rao B. Lung and colon cancer classification using hybrid principle component analysis network-extreme learning machine. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2023;35:e7361. doi: 10.1002/cpe.7361. - DOI
-
- Ragab M., Abdushkour H.A., Nahhas A.F., Aljedaibi W.H. Deer hunting optimization with deep learning model for lung cancer classification. CMC Comput. Mater. Continua. 2022;73:533–546. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2022.028856. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

