Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma Cancers Using Chlorotoxin Nanoparticles
- PMID: 37444498
- PMCID: PMC10341066
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15133388
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Glioblastoma and Neuroblastoma Cancers Using Chlorotoxin Nanoparticles
Abstract
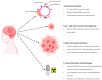
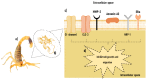
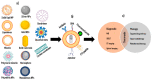
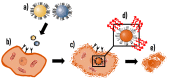
Glioblastoma multiforme (GB) and high-risk neuroblastoma (NB) are known to have poor therapeutic outcomes. As for most cancers, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the current mainstay treatments for GB and NB. However, the known limitations of systemic toxicity, drug resistance, poor targeted delivery, and inability to access the blood-brain barrier (BBB), make these treatments less satisfactory. Other treatment options have been investigated in many studies in the literature, especially nutraceutical and naturopathic products, most of which have also been reported to be poorly effective against these cancer types. This necessitates the development of treatment strategies with the potential to cross the BBB and specifically target cancer cells. Compounds that target the endopeptidase, matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2), have been reported to offer therapeutic insights for GB and NB since MMP-2 is known to be over-expressed in these cancers and plays significant roles in such physiological processes as angiogenesis, metastasis, and cellular invasion. Chlorotoxin (CTX) is a promising 36-amino acid peptide isolated from the venom of the deathstalker scorpion, Leiurus quinquestriatus, demonstrating high selectivity and binding affinity to a broad-spectrum of cancers, especially GB and NB through specific molecular targets, including MMP-2. The favorable characteristics of nanoparticles (NPs) such as their small sizes, large surface area for active targeting, BBB permeability, etc. make CTX-functionalized NPs (CTX-NPs) promising diagnostic and therapeutic applications for addressing the many challenges associated with these cancers. CTX-NPs may function by improving diffusion through the BBB, enabling increased localization of chemotherapeutic and genotherapeutic drugs to diseased cells specifically, enhancing imaging modalities such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), optical imaging techniques, image-guided surgery, as well as improving the sensitization of radio-resistant cells to radiotherapy treatment. This review discusses the characteristics of GB and NB cancers, related treatment challenges as well as the potential of CTX and its functionalized NP formulations as targeting systems for diagnostic, therapeutic, and theranostic purposes. It also provides insights into the potential mechanisms through which CTX crosses the BBB to bind cancer cells and provides suggestions for the development and application of novel CTX-based formulations for the diagnosis and treatment of GB and NB in the future.
Keywords: blood-brain-barrier (BBB); chlorotoxin (CTX); glioblastoma (GB); matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2); nanoparticles (NPs); neuroblastoma (NB).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ayed A.S., Omran M.A.A.A., Nabil Z., Strong P., Newton K., Abdel Rahman M. GBD 2017 US Neurological Disorders Collaborators Burden of Neurological Disorders Across the US from 1990–2017: A Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78:165–176. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohammadi E., Ghasemi E., Azadnajafabad S., Rezaei N., Moghaddam S.S., Meimand S.E., Fattahi N., Habibi Z., Yarandi K.K., Amirjamshidi A., et al. A global, regional, and national survey on burden and Quality of Care Index (QCI) of brain and other central nervous system cancers; global burden of disease systematic analysis 1990–2017. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0247120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

