Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance
- PMID: 37444501
- PMCID: PMC10341343
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15133390
Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance
Abstract
The involvement of glucose metabolic reprogramming in breast cancer progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance has been increasingly appreciated. Studies in recent years have revealed molecular mechanisms by which glucose metabolic reprogramming regulates breast cancer. To date, despite a few metabolism-based drugs being tested in or en route to clinical trials, no drugs targeting glucose metabolism pathways have yet been approved to treat breast cancer. Here, we review the roles and mechanisms of action of glucose metabolic reprogramming in breast cancer progression and drug resistance. In addition, we summarize the currently available metabolic inhibitors targeting glucose metabolism and discuss the challenges and opportunities in targeting this pathway for breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Warburg effect; breast cancer; drug resistance; glucose metabolism; metabolic inhibitor; metastasis; reverse Warburg effect; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
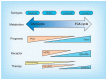
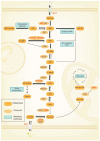
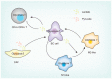
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

