One Pandemic, Two Solutions: Comparing the U.S.-China Response and Health Priorities to COVID-19 from the Perspective of "Two Types of Control"
- PMID: 37444682
- PMCID: PMC10341116
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11131848
One Pandemic, Two Solutions: Comparing the U.S.-China Response and Health Priorities to COVID-19 from the Perspective of "Two Types of Control"
Abstract
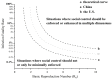
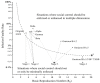
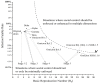
After three years of global rampage, the COVID-19 epidemic, the most serious infectious disease to occur worldwide since the 1918 influenza pandemic, is nearing its end. From the global experience, medical control and social control are the two main dimensions in the prevention and control of COVID-19. From the perspective of "two types of control", namely medical control and social control, this paper finds that the political system, economic structure, and cultural values of the United States greatly limit the government's ability to impose social control, forcing it to adopt medical control to fight the virus in a single dimension. In contrast, China's political system, economic structure, and cultural values allow its government to adopt stringent, extensive, and frequent social control, as well as medical control to fight the virus. This approach departs from the traditional pathway of fighting the epidemic, i.e., "infection-treatment-immunization", thereby outpacing the evolution of the virus and controlling its spread more rapidly. This finding helps explain why the Chinese government adopted a strict "zeroing" and "dynamic zeroing" policy during the first three years, at the cost of enormous economic, social, and even political legitimacy. It was not until late 2022, when the Omicron variant with the waning virulence became prevalent, that China chose to "coexist" with the virus, thus avoiding a massive epidemic-related death. While the United States adopted a pulsed-style strategy at the beginning of the epidemic, i.e., "relaxation-suppression-relaxation-suppression", and began to "coexist" with the virus in just one year, resulting in a large number of excess deaths associated with the epidemic. The study contributes to explaining the difference in the interplay between public health priorities and COVID-19 response strategies in China and the United States, based on the specific public health context and the perspective of "medical control" and "social control".
Keywords: COVID-19; coexistence policy; medical control; social control; zeroing policy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
China's Public Health Policies in Response to COVID-19: From an "Authoritarian" Perspective.Front Public Health. 2021 Dec 15;9:756677. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.756677. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34976920 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental management strategy in response to COVID-19 in China: Based on text mining of government open information.Sci Total Environ. 2021 May 15;769:145158. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145158. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33485207 Free PMC article.
-
Public Health Crises In Comparison: China's Epidemic Response Policies From SARS To COVID-19.Glob Public Health. 2021 Aug-Sep;16(8-9):1223-1236. doi: 10.1080/17441692.2021.1919735. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Glob Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33891518
-
COVID-19 Containment: Comparisons and Suggestions for Global Response.Inquiry. 2022 Jan-Dec;59:469580221086142. doi: 10.1177/00469580221086142. Inquiry. 2022. PMID: 35584986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response to COVID-19 in the Central African Republic: Coping Strategies Combined With China's Experience.Int J Public Health. 2022 Apr 25;67:1604344. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1604344. eCollection 2022. Int J Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35548685 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The global response to the pandemic: An empirical cluster analysis of policies targeting COVID-19.PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0322692. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322692. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40373002 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Baseline Echocardiographic Parameters and Acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection in Hospitalized Patients.Cureus. 2024 Mar 3;16(3):e55432. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55432. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38567218 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Insights: Unraveling Public Demand Evolution in Health Emergencies Through Integrated Language Models and Spatial-Temporal Analysis.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024 Oct 18;17:2443-2455. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S472247. eCollection 2024. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2024. PMID: 39439579 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of state-level policy responses in global health governance: A scoping review using COVID-19 as a case.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 7;19(11):e0313430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313430. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39509448 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the efficacy of COVID-19 responses in South Korea and the United States.Glob Health Action. 2024 Dec 31;17(1):2370611. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2024.2370611. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Glob Health Action. 2024. PMID: 39135484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization [(accessed on 11 May 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/data.
-
- World Health Organization [(accessed on 15 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/stories/global-excess-deaths-associated-with-co...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

