Racial/Ethnic Patterns in Opioid Dispensing among Medicaid-Funded Young Children
- PMID: 37444744
- PMCID: PMC10341251
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11131910
Racial/Ethnic Patterns in Opioid Dispensing among Medicaid-Funded Young Children
Abstract
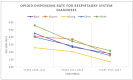
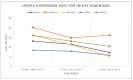
Racial differences in opioid dispensing for diseases of the respiratory system (RESP) and injury (INJURY) outpatient visits among patients ≤ 3 years old were examined. Outpatient claims data of South Carolina Medicaid children were analyzed over three three-year periods. The variable of interest was the triennial rate of dispensed opioid prescriptions per 1000 visits for RESP and INJURY diagnoses across racial/ethnic groups. Overall, dispensed opioid prescription rates related to RESP declined for all racial/ethnic categories. White children had the highest dispensing rate for RESP indications in the first period (5.6), followed by Black (4.5), and Hispanic (4.1). The likelihood of White children being prescribed opioids was higher than Blacks, and this was persistent over the studied time (rate ratios from 1.24 to 1.22, respectively). Overall opioid dispensing rates related to injury declined during the studied time. Hispanics had the highest dispensing rate for INJURY (20.1 to 14.8 to 16.1, respectively) followed by White (16.1 to 13.1 to 10.4, respectively). Relative differences in the dispensing rates across groups increased over time (Hispanics vs. White: rate ratios from 1.25 to 1.55, Hispanics vs. Black: from 1.52 to 2.24, and White vs. Black: from 1.24 to 1.44, respectively). There are considerable differences in the dispensing rates across racial/ethnic groups, especially in injury-related prescribing.
Keywords: Medicaid; diseases of the respiratory system; injury; prescription opioids; race/ethnicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Conradt E., Flannery T., Aschner J.L., Annett R.D., Croen L.A., Duarte C.S., Friedman A.M., Guille C., Hedderson M.M., Hofheimer J.A., et al. Prenatal opioid exposure: Neurodevelopmental Consequences and Future Research Priorities. Pediatrics. 2019;144:e20190128. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0128. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

