Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health
- PMID: 37444780
- PMCID: PMC10340576
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11131946
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health
Abstract
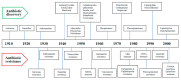
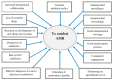
Antibiotics are among the most important discoveries of the 20th century, having saved millions of lives from infectious diseases. Microbes have developed acquired antimicrobial resistance (AMR) to many drugs due to high selection pressure from increasing use and misuse of antibiotics over the years. The transmission and acquisition of AMR occur primarily via a human-human interface both within and outside of healthcare facilities. A huge number of interdependent factors related to healthcare and agriculture govern the development of AMR through various drug-resistance mechanisms. The emergence and spread of AMR from the unrestricted use of antimicrobials in livestock feed has been a major contributing factor. The prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria has attained an incongruous level worldwide and threatens global public health as a silent pandemic, necessitating urgent intervention. Therapeutic options of infections caused by antimicrobial-resistant bacteria are limited, resulting in significant morbidity and mortality with high financial impact. The paucity in discovery and supply of new novel antimicrobials to treat life-threatening infections by resistant pathogens stands in sharp contrast to demand. Immediate interventions to contain AMR include surveillance and monitoring, minimizing over-the-counter antibiotics and antibiotics in food animals, access to quality and affordable medicines, vaccines and diagnostics, and enforcement of legislation. An orchestrated collaborative action within and between multiple national and international organizations is required urgently, otherwise, a postantibiotic era can be a more real possibility than an apocalyptic fantasy for the 21st century. This narrative review highlights on this basis, mechanisms and factors in microbial resistance, and key strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Keywords: antibiotics; antimicrobial resistance; drivers of resistance; measures to combat resistance; mechanisms of resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- CDC How Antimicrobial Resistance Happens. [(accessed on 2 June 2023)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about/how-resistance-happens.html.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources