Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Cesium Ions in Low-Concentration Brine Using Ammonium Molybdophosphate-Zirconium Phosphate on Polyurethane Sponge
- PMID: 37444898
- PMCID: PMC10343003
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16134583
Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Cesium Ions in Low-Concentration Brine Using Ammonium Molybdophosphate-Zirconium Phosphate on Polyurethane Sponge
Abstract
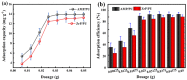
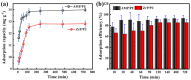
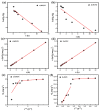
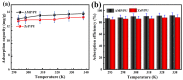
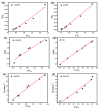
Salt lake brine originating from Qinghai, China has abundant cesium resources and huge total reserves. The inorganic ion exchangers ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP) and zirconium phosphate (ZrP) have the significant advantages of separating and extracting Cs+ as a special adsorbent. Nevertheless, their high solubility in water leads to a decrease in their ability to adsorb Cs+ in aqueous solutions, causing problems such as difficulty with using adsorbents alone and a difficult recovery. In this work, an environmentally friendly polyurethane sponge (PU sponge) with a large specific surface area is employed as an adsorbent carrier by physically impregnating dopamine-coated AMP and ZrP onto a PU sponge, respectively. The experiment found that under the same conditions, the AMP/PU sponge performs better than the ZrP/PU sponge for Cs+ adsorption. When the amount of adsorbent reaches 0.025 g, the adsorption capacity reaches saturation. The adsorption efficiency remains above 80% when the concentration of Cs+ is 5-35 mg/L. The kinetic calculations show that adsorption is spontaneous, feasible, and has a higher driving force at high temperatures. In addition, the power and mechanism of the interaction between adsorbent and adsorbent are explained using the density functional theory calculation. This efficient, stable, and selective Cs+ adsorbent provides design guidelines.
Keywords: Cs+ adsorption; ammonium molybdophosphate; polyurethane sponge; zirconium phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Hang S., Lingdan Z., Qi L., Shujun G., Zhang H. Urushiol-resourced dopamine analogue as a trigger to construct clay-hexacyanoferrate hydrogel for cesium removal. J. Environ. Eng. 2021;9:106140–106151.
-
- He F., Song E., Zhou Y., Ming H., Chen Z., Wu J., Shao P., Yang X., Xia Z., Zhang Q. A general ammonium salt assisted synthesis strategy for Cr3+-doped hexafluorides with highly efficient near infrared emissions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2103743–2103754. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202103743. - DOI
-
- Gao L., Ma G., Zheng Y., Tang Y., Xie G., Yu J., Liu B., Duan J. Research Trends on Separation and Extraction of Rare Alkali Metal from Salt Lake Brine: Rubidium and Cesium. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2020;38:753–776. doi: 10.1080/07366299.2020.1802820. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

