Design and Development of Low- and Medium-Viscosity Alginate Beads Loaded with Pluronic® F-127 Nanomicelles
- PMID: 37445029
- PMCID: PMC10342433
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16134715
Design and Development of Low- and Medium-Viscosity Alginate Beads Loaded with Pluronic® F-127 Nanomicelles
Abstract
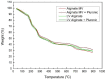
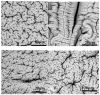
The anionic polymer sodium alginate, a linear copolymer of guluronic and mannuronic acids, is primarily present in brown algae. Copolymers are used in the sodium alginate preparation process to confer on the material strength and flexibility. Micelles and other polymeric nanoparticles are frequently made using the triblock copolymer Pluronic® F-127. The purpose of the present study is to determine the effect of sodium alginate's viscosity (low and medium) and the presence of Pluronic® F-127 micelles on the swelling behavior of the prepared pure beads and those loaded with Pluronic® F-127 micelles. The Pluronic® F-127 nanomicelles have a size of 120 nm. The swelling studies were carried out at pH = 1.2 (simulated gastric fluid-SGF) for two hours and at pH = 6.8 (simulated intestinal fluid-SIF) for four more hours. The swelling of both low- and medium-viscosity alginate beads was minor at pH = 1.2, irrespective of the use of Pluronic® F-127 nanomicelles. At pH = 6.8, without Pluronic® F-127, the beads showed an enhanced swelling ratio for the first four hours, which was even higher in the medium-viscosity alginate beads. With the addition of Pluronic® F-127, the beads were dissolved in the first and second hour, in the case of the low- and medium-alginate's viscosity, respectively. In other words, the behavior of the mixed hydrogels was the same during the swelling experiments. Therefore, the presence of Pluronic® F-127 nanomicelles and medium-viscosity sodium alginate leads to a higher swelling ratio. A model drug, acetyl salicylic acid (ASA), was also encapsulated in the mixed beads and ASA's release studies were performed. In conclusion, the prepared systems, which are well characterized, show potential as delivery platforms for the oral delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients and biopharmaceuticals.
Keywords: Pluronic® F-127; acetyl salicylic acid; alginate beads; crosslinking; hydrogels; micelles; swelling studies; viscosity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oral delivery of insulin from alginate/chitosan crosslinked by glutaraldehyde.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013 Jul;58:160-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.03.064. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013. PMID: 23567292
-
Mechanisms of formation and disintegration of alginate beads obtained by prilling.Int J Pharm. 2005 Sep 30;302(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.05.041. Int J Pharm. 2005. PMID: 16102925
-
Effect of alginate composition and gelling cation on micro-bead swelling.J Microencapsul. 2006 Feb;23(1):29-37. doi: 10.1080/02652040500286144. J Microencapsul. 2006. PMID: 16830975
-
Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: alginate and chitosan--a review.J Control Release. 2006 Aug 10;114(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.04.017. Epub 2006 May 22. J Control Release. 2006. PMID: 16828914 Review.
-
Nanoparticle-loaded bioactive hydrogels.In: König K, Ostendorf A, editors. Optically Induced Nanostructures: Biomedical and Technical Applications. Berlin: De Gruyter; 2015 Jun 23. Chapter 4. In: König K, Ostendorf A, editors. Optically Induced Nanostructures: Biomedical and Technical Applications. Berlin: De Gruyter; 2015 Jun 23. Chapter 4. PMID: 26491766 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Fabricating Polymer/Surfactant/Cyclodextrin Hybrid Particles for Possible Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Ropinirole Hydrochloride: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 18;25(2):1162. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021162. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256239 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Modified Release Studies on Melatoninergic Fluorinated Phenylalkylamides: Circumventing their Lipophilicity for Oral Administration.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(18):1433-1441. doi: 10.2174/0113816128304967240328065809. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38616752
References
-
- Pippa N., Sentoukas T., Pispas S., Demetzos C., Papalois A., Bouropoulos N. PH-Responsive Polymeric Nanoassemblies Encapsulated into Alginate Beads: Morphological Characterization and Swelling Studies. J. Polym. Res. 2018;25:117. doi: 10.1007/s10965-018-1519-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

