Effect of Sandblasting Parameters and the Type and Hardness of the Material on the Number of Embedded Al2O3 Grains
- PMID: 37445098
- PMCID: PMC10343725
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16134783
Effect of Sandblasting Parameters and the Type and Hardness of the Material on the Number of Embedded Al2O3 Grains
Abstract
Background: Is abrasive blasting accompanied by the phenomenon of driving abrasive particles into the conditioned material?
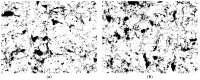
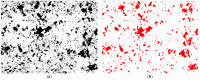
Methods: Three hundred and fifteen cylindrical disks of three types of metal alloy (chromium/cobalt, chromium/nickel, titanium, and sintered zirconium dioxide) were divided into four groups (n = 35) and sandblasted at pressures of 0.2, 0.4, or 0.6 MPa with aluminum oxide (Al2O3), grain size 50, 110, or 250 μm. Then, the surface topography was examined using a scanning microscope, and the amount of embedded grain was measured using quantitative metallography. For each group, five samples were randomly selected and subjected to Vickers hardness testing. In the statistical analyses, a three-factor analysis of variance was carried out, considering the type of material, the size of gradation of the abrasive, and the amount of pressure.
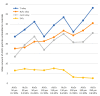
Results: The smallest amounts of embedded abrasive (2.62) were observed in the ZrO2 treatment, and the largest (38.19) occurred in the treatment of the Ti alloy. An increase in the gradation and the pressure were a systematic increase in the amount of embedded grain.
Conclusions: After abrasive blasting, abrasive particles were found on the surface of the materials. The amount of driven abrasive depends on the hardness of the processed material.
Keywords: Cr/Co alloy; Ni/Cr alloy; Ti; ZrO2; abrasive blasting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Influence of Material Type and Hardness on the Number of Embedded Abrasive Particles during Airborne-Particle Abrasion.Materials (Basel). 2022 Apr 11;15(8):2794. doi: 10.3390/ma15082794. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454487 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Ni-Cr Alloy Surface Abrasive Blasting on Its Wettability by Liquid Ceramics.Materials (Basel). 2021 Apr 16;14(8):2007. doi: 10.3390/ma14082007. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923646 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Air Abrasion on the Number of Particles Embedded in Zironia.Materials (Basel). 2018 Feb 8;11(2):259. doi: 10.3390/ma11020259. Materials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29419729 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of the Ceramic and Ni-Cr Alloy Joint after Al2O3 Abrasive Blasting.Materials (Basel). 2023 May 17;16(10):3800. doi: 10.3390/ma16103800. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37241426 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of abrasive blasting on the strength of a joint between dental porcelain and metal base.Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2014;16(1):63-8. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2014. PMID: 24708248
Cited by
-
Advanced Materials for Oral Application (Volume 2).Materials (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;18(5):1042. doi: 10.3390/ma18051042. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40077268 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-shear bond strength of a novel resin-modified glass ionomer luting cement (eRMGIC) functionalized with organophosphorus monomer to different dental substrates.Heliyon. 2024 May 7;10(9):e30851. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30851. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38765086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan A.A., Haque M.M. Performance of different abrasive materials during abrasive water jet machining of glass. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2007;191:404–407. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.03.071. - DOI
-
- Gołębiowski M., Sobczyk-Guzenda A., Szymański W., Klimek L. Influence of parameters of stream abrasive treatment of titanium surfaces on contact angle and surface free energy. Mater. Eng. 2010;173:978–980.
-
- Pietnicki K., Wołowiec E., Klimek L. The effect of abrasive blasting on the strength of a joint between dental porcelain and metal base. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2014;16:63–68. - PubMed
-
- Białucki P., Kozerski S. Study of adhesion of different plasma-sprayed coatings to aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006;201:2061–2064. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.04.043. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

