Cerebral Oxygenation Responses to Standing in Young Patients with Vasovagal Syncope
- PMID: 37445237
- PMCID: PMC10342995
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12134202
Cerebral Oxygenation Responses to Standing in Young Patients with Vasovagal Syncope
Abstract
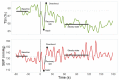
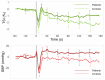
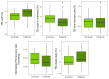
Vasovagal syncope (VVS) is common in young adults and is attributed to cerebral hypoperfusion. However, during active stand (AS) testing, only peripheral and not cerebral hemodynamic responses are measured. We sought to determine whether cerebral oxygenation responses to an AS test were altered in young VVS patients when compared to the young healthy controls. A sample of young healthy adults and consecutive VVS patients attending a Falls and Syncope unit was recruited. Continuous beat-to-beat blood pressure (BP), heart rate, near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS)-derived tissue saturation index (TSI), and changes in concentration of oxygenated/deoxygenated Δ[O2Hb]/Δ[HHb] hemoglobin were measured. BP and NIRS-derived features included nadir, peak, overshoot, trough, recovery rate, normalized recovery rate, and steady-state. Multivariate linear regression was used to adjust for confounders and BP. In total, 13 controls and 27 VVS patients were recruited. While no significant differences were observed in the TSI and Δ[O2Hb], there was a significantly smaller Δ[HHb] peak-to-trough and faster Δ[HHb] recovery rate in VVS patients, independent of BP. A higher BP steady-state was observed in patients but did not remain significant after multiple comparison correction. Young VVS patients demonstrated a similar cerebral circulatory response with signs of altered peripheral circulation with respect to the controls, potentially due to a hyper-reactive autonomic nervous system. This study sets the grounds for future investigations to understand the role of cerebral regulation during standing in VVS.
Keywords: cerebral oxygenation; near-infrared spectroscopy; orthostatic; standing; syncope; young.
Conflict of interest statement
C.F. is funded by Endotronix as part of an Industrial Partnership grant. All other authors report no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Carmody M., Finucane C., Nolan H., Kenny R.A. Combining the Active Stand Test and Pattern Recognition Methods to Predict Vasovagal Syncope. Trinity College Dublin; Dublin, Ireland: 2013.
-
- Sybring M., Finucane C., Nolan H., Kenny R.A. A Convenient Test for Vasovagal Syncope in Older Adults Combining Pattern Recognition and the Active Stand Test. Trinity College Dublin; Dublin, Ireland: 2014.
-
- Carmody M., Finucane C., Nolan H., O’Dwyer C., Kwok M., Kenny R.A., Fan C.W. A Machine Learning Framework to Detect Syncope using the Active Stand. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.12.07.20245159. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

