Nanofat in Plastic Reconstructive, Regenerative, and Aesthetic Surgery: A Review of Advancements in Face-Focused Applications
- PMID: 37445386
- PMCID: PMC10342690
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12134351
Nanofat in Plastic Reconstructive, Regenerative, and Aesthetic Surgery: A Review of Advancements in Face-Focused Applications
Abstract
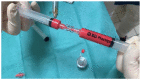
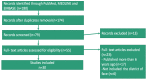
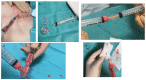
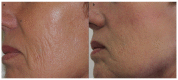
Nanofat is a relatively novel technique in fat grafting that has gained significant interest in the fields of regenerative medicine, aesthetic and translational research. It involves the extraction of autologous fat from a patient, which is then transformed into "nanofat", consisting of small fat particles with a diameter of less than 0.1 mm and containing high concentrations of stem cells and growth factors. This article focuses on the use of nanofat in facial rejuvenation and its potential for lipomodelling. Fat tissue is a "stem cell depot" and nanofat contains many stem cells that can differentiate into various cell types. The Lipogem technology, developed in 2013, enables the isolation of nanofat with an intact perivascular structure, utilizing the high concentration of mesenchymal stromal cells near the pericytes of the adipose vascular system. Nowadays nanofat is used primarily for cosmetic purposes particularly in rejuvenating and improving the appearance of the skin, especially the face. Indeed, it has wide applicability; it can be used to treat fine lines, wrinkles, acne scars, sun-damaged skin, scar repair, and as an alopecia treatment. However, further studies are needed to assess the long-term efficacy and safety of this technique. In conclusion, nanofat is a safe and minimally invasive option for tissue regeneration with considerable therapeutic potential. This study reviews the application and effects of nanofat in regenerative medicine and facial cosmetic surgery.
Keywords: a review; facial rejuvenation; fat graft; lipomodelling; nanofat; regenerative medicine; stromal vascular tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

