Clinical Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Bone Regeneration
- PMID: 37445420
- PMCID: PMC10342399
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12134385
Clinical Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Bone Regeneration
Abstract
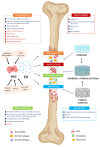
Bone metabolism is regulated by osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and stem cells. Pathologies such as osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, osteonecrosis, and traumatic fractures require effective treatments that favor bone formation and regeneration. Among these, cell therapy based on mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) has been proposed. MSC are osteoprogenitors, but their regenerative activity depends in part on their paracrine properties. These are mainly mediated by extracellular vesicle (EV) secretion. EV modulates regenerative processes such as inflammation, angiogenesis, cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Thus, MSC-EV are currently an important tool for the development of cell-free therapies in regenerative medicine. This review describes the current knowledge of the effects of MSC-EV in the different phases of bone regeneration. MSC-EV has been used by intravenous injection, directly or in combination with different types of biomaterials, in preclinical models of bone diseases. They have shown great clinical potential in regenerative medicine applied to bone. These findings should be confirmed through standardization of protocols, a better understanding of the mechanisms of action, and appropriate clinical trials. All that will allow the translation of such cell-free therapy to human clinic applications.
Keywords: biomaterials; bone; cell-free therapy; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal stem cells; regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) in Regenerative Medicine: Applications in Skin Wound Healing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Mar 3;8:146. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00146. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32195233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles and bone regeneration.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Jan;128(1):18-36. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13478. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32780530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in bone regenerative strategies-a systematic review of preclinical studies.Mater Today Bio. 2020 Jun 27;7:100067. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2020.100067. eCollection 2020 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2020. PMID: 32695985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles, osteoimmunology and orthopedic diseases.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 24;11:e14677. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14677. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36710868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes in Regenerative Medicine.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(6):482-494. doi: 10.2174/1574888X14666190228103230. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30819086 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanostructured Affinity Membrane to Isolate Extracellular Vesicles from Body Fluids for Diagnostics and Regenerative Medicine.Membranes (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;14(10):206. doi: 10.3390/membranes14100206. Membranes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452818 Free PMC article.
-
Morinda officinalis polysaccharide boosts osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):4492-4503. doi: 10.62347/WMLI2601. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39398614 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on allergic rhinitis in mice.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 19;11(1):e41340. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41340. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39816505 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering extracellular vesicles for ROS scavenging and tissue regeneration.Nano Converg. 2024 Jun 26;11(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40580-024-00430-9. Nano Converg. 2024. PMID: 38922501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of Klotho delivering mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles on acute kidney injury.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jun 7;23(1):427. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03499-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40481485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari N., Sims N.A. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Volume 262. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2020. The Cells of Bone and Their Interactions; pp. 1–25. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

