MRI-Conditional Breast Tissue Expander: First In-Human Multi-Case Assessment of MRI-Related Complications and Image Quality
- PMID: 37445444
- PMCID: PMC10342840
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12134410
MRI-Conditional Breast Tissue Expander: First In-Human Multi-Case Assessment of MRI-Related Complications and Image Quality
Abstract
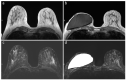
This study aims to assess potential complications and effects on the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image quality of a new MRI-conditional breast tissue expander (Motiva Flora®) in its first in-human multi-case application. Twenty-four patients with 36 expanders underwent non-contrast breast MRI with T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences on a 3 T unit before breast tissue expander exchange surgery, being monitored during and after MRI for potential complications. Three board-certified breast radiologists blindly and independently reviewed image quality using a four-level scale ("poor", "sufficient", "good", and "excellent"), with inter-reader reliability being assessed with Kendall's τb. The maximum diameters of RFID-related artifacts on T1-weighted and DWI sequences were compared with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. All 24 examinations were completed without patient-related or device-related complications. The T1-weighted and T2-weighted sequences of all the examinations had "excellent" image quality and a median 11 mm (IQR 9-12 mm) RFID artifact maximum diameter, significantly lower (p < 0.001) than on the DWI images (median 32.5 mm, IQR 28.5-34.5 mm). DWI quality was rated at least "good" in 63% of the examinations, with strong inter-reader reliability (Kendall's τb 0.837, 95% CI 0.687-0.952). This first in-human study confirms the MRI-conditional profile of this new expander, which does not affect the image quality of T1-weighted and T2-weighted sequences and moderately affects DWI quality.
Keywords: MRI safety; MRI-conditional; artifacts; breast reconstruction; breast tissue expander; diffusion-weighted imaging; image quality; magnetic resonance imaging; mastectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Simone Schiaffino declares to have received travel support from Bracco Imaging, to be a member of the speakers’ bureau for GE Healthcare, and to be a product advisor for Arterys. Yves Harder declares to have received travel support from Establishment Labs. All other authors declare they have no conflict of interest and that they have nothing to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Breast Tissue Expander With Radiofrequency Identification Port: Assessment of MRI Issues.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 Jul;215(1):159-164. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.22492. Epub 2020 May 14. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020. PMID: 32406774
-
Clinical and MRI Evaluation of Silicone Gel Implants with RFID-M Traceability System: A Prospective Controlled Cohort Study Related to Safety and Image Quality in MRI Follow-Up.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021 Dec;45(6):2645-2655. doi: 10.1007/s00266-021-02355-8. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34075463
-
Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Breast Cancer: Improved Lesion Visibility and Image Quality Using Synthetic b-Values.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Dec;50(6):1754-1761. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26809. Epub 2019 May 28. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31136044 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value and safety of dynamic MRI of contralateral breast and axilla in subjects with tissue expander.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018 Sep;71(9):1282-1285. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 Jun 8. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018. PMID: 29983366 Review.
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in patients with magnetic resonance conditional pacemaker systems at 1.5 T: influence of pacemaker related artifacts on image quality including first pass perfusion, aortic and mitral valve assessment, flow measurement, short tau inversion recovery and T1-weighted imaging.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017 Mar;33(3):383-394. doi: 10.1007/s10554-016-1012-z. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27815793 Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging of the Reconstructed Breast.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;13(20):3186. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203186. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smooth Operator: Nanotextured Breast Tissue Expanders Are Associated with Lower Rates of Capsular Contracture.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 28;13(19):5803. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195803. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407864 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated Autologous Fat Grafting Significantly Increases Mastectomy Flap Thickness in Pre-Pectoral Multi-Stage Composite Expander-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction: Exploring the Concept of a Reverse Expansion.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 8;14(2):337. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020337. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manahan E.R., Kuerer H.M., Sebastian M., Hughes K.S., Boughey J.C., Euhus D.M., Boolbol S.K., Taylor W.A. Consensus Guidelines on Genetic’ Testing for Hereditary Breast Cancer from the American Society of Breast Surgeons. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019;26:3025–3031. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07549-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

