Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson's Disease: An Overview on Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, Therapy Management Strategies and Future Directions
- PMID: 37445461
- PMCID: PMC10342913
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12134427
Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson's Disease: An Overview on Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, Therapy Management Strategies and Future Directions
Abstract
Since its first introduction, levodopa has become the cornerstone for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and remains the leading therapeutic choice for motor control therapy so far. Unfortunately, the subsequent appearance of abnormal involuntary movements, known as dyskinesias, is a frequent drawback. Despite the deep knowledge of this complication, in terms of clinical phenomenology and the temporal relationship during a levodopa regimen, less is clear about the pathophysiological mechanisms underpinning it. As the disease progresses, specific oscillatory activities of both motor cortical and basal ganglia neurons and variation in levodopa metabolism, in terms of the dopamine receptor stimulation pattern and turnover rate, underlie dyskinesia onset. This review aims to provide a global overview on levodopa-induced dyskinesias, focusing on pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, therapy management strategies and future directions.
Keywords: LIDs; Parkinson’s disease; clinical manifestations; levodopa-induced dyskinesias; motor complications; pathophysiology; therapy management.
Conflict of interest statement
L. di Biase is the scientific director and one of the shareholders of Brain Innovations Srl, a University spinoff of the Campus Bio-Medico University of Rome. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
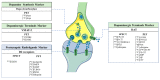
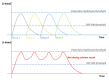
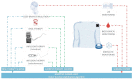
References
-
- Hechtner M.C., Vogt T., Zollner Y., Schroder S., Sauer J.B., Binder H., Singer S., Mikolajczyk R. Quality of life in Parkinson’s disease patients with motor fluctuations and dyskinesias in five European countries. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014;20:969–974. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.06.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

