Emerging Role of GLP-1 Agonists in Obesity: A Comprehensive Review of Randomised Controlled Trials
- PMID: 37445623
- PMCID: PMC10341852
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310449
Emerging Role of GLP-1 Agonists in Obesity: A Comprehensive Review of Randomised Controlled Trials
Abstract
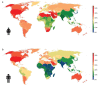
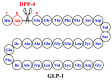
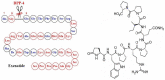
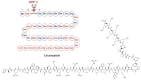
Obesity is a chronic disease with high prevalence and associated comorbidities, making it a growing global concern. These comorbidities include type 2 diabetes, hypertension, ventilatory dysfunction, arthrosis, venous and lymphatic circulation diseases, depression, and others, which have a negative impact on health and increase morbidity and mortality. GLP-1 agonists, used to treat type 2 diabetes, have been shown to be effective in promoting weight loss in preclinical and clinical studies. This review summarizes numerous studies conducted on the main drugs in the GLP-1 agonists class, outlining the maximum achievable weight loss. Our aim is to emphasize the active role and main outcomes of GLP-1 agonists in promoting weight loss, as well as in improving hyperglycemia, insulin sensitivity, blood pressure, cardio-metabolic, and renal protection. We highlight the pleiotropic effects of these medications, along with their indications, contraindications, and precautions for both diabetic and non-diabetic patients, based on long-term follow-up studies.
Keywords: GLP-1 agonists; Lixisenatide; exenatide; liraglutide; obesity; semaglutide; tirzepatide; type 2 diabetes; weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

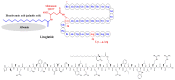
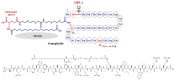
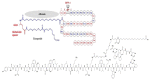
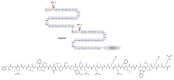
References
-
- Ritchie H., Roser M. “Obesity”. Published online at OurWorldInData.org. 2017. [(accessed on 10 January 2023)]. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/obesity.
-
- Apovian C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2016;22((Suppl. S7)):s176–s185. - PubMed
-
- WHO European Regional Obesity Report 2022. WHO Regional Office for Europe; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2022.
-
- Roman G., Bala C., Creteanu G., Graur M., Morosanu M., Amorin P., Pîrcalaboiu L., Radulian G., Timar R., Cadariu A.A. Obesity and Health-Related lifestyle factors in the general population in romania: A cross sectional study. Acta Endocrinol. 2015;11:64–71. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2015.64. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

