Enhancing Cementitious Composites with Functionalized Graphene Oxide-Based Materials: Surface Chemistry and Mechanisms
- PMID: 37445640
- PMCID: PMC10341748
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310461
Enhancing Cementitious Composites with Functionalized Graphene Oxide-Based Materials: Surface Chemistry and Mechanisms
Abstract
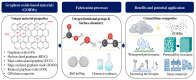
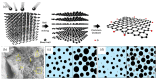
Graphene oxide-based materials (GOBMs) have been widely explored as nano-reinforcements in cementitious composites due to their unique properties. Oxygen-containing functional groups in GOBMs are crucial for enhancing the microstructure of cementitious composites. A better comprehension of their surface chemistry and mechanisms is required to advance the potential applications in cementitious composites of functionalized GOBMs. However, the mechanism by which the oxygen-containing functional groups enhance the response of cementitious composites is still unclear, and controlling the surface chemistry of GOBMs is currently constrained. This review aims to investigate the reactions and mechanisms for functionalized GOBMs as additives incorporated in cement composites. A variety of GOBMs, including graphene oxide (GO), hydroxylated graphene (HO-G), edge-carboxylated graphene (ECG), edge-oxidized graphene oxide (EOGO), reduced graphene oxide (rGO), and GO/silane composite, are discussed with regard to their oxygen functional groups and interactions with the cement microstructure. This review provides insight into the potential benefits of using GOBMs as nano-reinforcements in cementitious composites. A better understanding of the surface chemistry and mechanisms of GOBMs will enable the development of more effective functionalization strategies and open up new possibilities for the design of high-performance cementitious composites.
Keywords: cementitious composites; graphene oxide-based materials; nano-reinforced materials; oxygen functional groups; surface chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Mokhtar M., Abo-El-Enein S., Hassaan M., Morsy M., Khalil M. Mechanical performance, pore structure and micro-structural characteristics of graphene oxide nano platelets reinforced cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017;138:333–339. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.021. - DOI
-
- Zhao L., Zhu S., Wu H., Zhang X., Tao Q., Song L., Song Y., Guo X. Deep research about the mechanisms of graphene oxide (GO) aggregation in alkaline cement pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020;247:118446. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118446. - DOI
-
- Yin B., Xu T., Hou D., Zhao E., Hua X., Han K., Zhang Y., Zhang J. Superhydrophobic anticorrosive coating for concrete through in-situ bionic induction and gradient mineralization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020;257:119510. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119510. - DOI
-
- Zhou Z., Li S., Cao J., Chen X., Wu Z., Zhou P. The waterproofing effect and mechanism of graphene oxide/silane composite emulsion on cement-based materials under compressive stress. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;308:124945. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124945. - DOI
-
- Chen X., Zhang Y., Li S., Geng Y., Hou D. Influence of a new type of graphene oxide/silane composite emulsion on the permeability resistance of damaged concrete. Coatings. 2021;11:208. doi: 10.3390/coatings11020208. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

