The Review of Current Knowledge on Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)
- PMID: 37445650
- PMCID: PMC10341718
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310470
The Review of Current Knowledge on Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)
Abstract
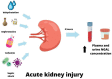
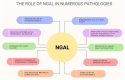
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a 25-kDa protein that is secreted mostly by immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Its production is stimulated in response to inflammation. The concentrations of NGAL can be measured in plasma, urine, and biological fluids such as peritoneal effluent. NGAL is known mainly as a biomarker of acute kidney injury and is released after tubular damage and during renal regeneration processes. NGAL is also elevated in chronic kidney disease and dialysis patients. It may play a role as a predictor of the progression of renal function decreases with complications and mortality due to kidney failure. NGAL is also useful in the diagnostic processes of cardiovascular diseases. It is highly expressed in injured heart tissue and atherosclerostic plaque; its serum concentrations correlate with the severity of heart failure and coronary artery disease. NGAL increases inflammatory states and its levels rise in arterial hypertension, obesity, diabetes, and metabolic complications such as insulin resistance, and is also involved in carcinogenesis. In this review, we present the current knowledge on NGAL and its involvement in different pathologies, especially its role in renal and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: NGAL; acute kidney injury; cardiovascular complications; chronic kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Latouche C., El Moghrabi S., Messaoudi S., Nguyen Dinh Cat A., Hernandez-Diaz I., Alvarez de la Rosa D., Perret C., López Andrés N., Rossignol P., Zannad F., et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a novel mineralocorticoid target in the cardiovascular system. Hypertension. 2012;59:966–972. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.187872. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eilenberg W., Stojkovic S., Piechota-Polanczyk A., Kaun C., Rauscher S., Gröger M., Klinger M., Wojta J., Neumayer C., Huk I., et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) is Associated with Symptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis and Drives Pro-inflammatory State In Vitro. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2016;51:623–631. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2016.01.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

