Recent Insight about HE4 Role in Ovarian Cancer Oncogenesis
- PMID: 37445657
- PMCID: PMC10341457
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310479
Recent Insight about HE4 Role in Ovarian Cancer Oncogenesis
Abstract
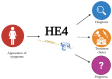
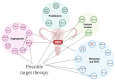
Currently, ovarian cancer (OC) is a target of intense biomarkers research because of its frequent late diagnosis and poor prognosis. Serum determination of Human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) is a very important early detection test. Most interestingly, HE4 plays a unique role in OC as it has been implicated not only in OC diagnosis but also in the prognosis and recurrence of this lethal neoplasm, actually acting as a clinical biomarker. There are several evidence about the predictive power of HE4 clinically, conversely less has been described concerning its role in OC oncogenesis. Based on these considerations, the main goal of this review is to clarify the role of HE4 in OC proliferation, angiogenesis, metastatization, immune response and also in the development of targeted therapy. Through a deeper understanding of its functions as a key molecule in the oncogenetic processes underlying OC, HE4 could be possibly considered as an essential resource not only for diagnosis but also for prognosis and therapy choice.
Keywords: HE4; oncogenesis; ovarian cancer; target therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

