Effect of Paclobutrazol Application on Enhancing the Efficacy of Nitenpyram against the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens
- PMID: 37445669
- PMCID: PMC10341613
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310490
Effect of Paclobutrazol Application on Enhancing the Efficacy of Nitenpyram against the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens
Abstract
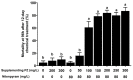
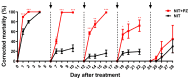
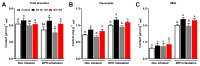
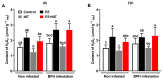
The brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens, is one of the most destructive rice pests in Asia. It has already developed a high level of resistance to many commonly used insecticides including nitenpyram (NIT), which is a main synthetic insecticide that is used to control BPH with a much shorter persistence compared to other neonicotinoid insecticides. Recently, we found that an exogenous supplement of paclobutrazol (PZ) could significantly enhance the efficacy of NIT against BPH, and the molecular mechanism underlying this synergistic effect was explored. The results showed that the addition of a range of 150-300 mg/L PZ increased the toxicity of NIT against BPH with the highest mortalities of 78.0-87.0% on the 16th day after treatments, and PZ could also significantly prolong the persistence of the NIT efficacies. Further investigation suggested that PZ directly increased the content of flavonoids and H2O2 in rice and increased the activity of polyphenol oxidase, which might be involved in the constitutive defense of rice in advance. Additionally, there was an interaction between PZ and BPH infestation, indicating that PZ might activate the host defense responses. Therefore, PZ increased the efficacy of NIT against the brown planthoppers by enhancing the constitutive and inducible defense responses of rice. Our study showed for the first time that PZ could contribute to improving the control effects of insecticides via inducing the defense responses in rice plants against BPH, which provided an important theoretical basis for developing novel pest management strategies in the field.
Keywords: Nilaparvata lugens; hydrogen peroxide; nitenpyram; paclobutrazol; synergetic effect; total phenolic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Area-wide survey and monitoring of insecticide resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), from 2020 to 2023 in China.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024 Nov;205:106173. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2024.106173. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39477626
-
Various functions of detoxification enzymes against insecticides in Nilaparvata lugens selected by toxicity assays and RNAi methods.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024 Jun;202:105939. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2024.105939. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38879330
-
Cross-Resistance and Baseline Susceptibility of Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) From China to Cycloxaprid.J Econ Entomol. 2018 Sep 26;111(5):2359-2363. doi: 10.1093/jee/toy222. J Econ Entomol. 2018. PMID: 30085244
-
Recent Advances in the Genetic and Biochemical Mechanisms of Rice Resistance to Brown Planthoppers (Nilaparvata lugens Stål).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 30;24(23):16959. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316959. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and molecular understanding of host rice resistance and Nilaparvata lugens adaptation.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2021 Jun;45:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2020.11.005. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2021. PMID: 33227482 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide characterization of GRF-GIF transcriptional modules in kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) reveals their roles in plant development and multi-stress adaptation.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 May 30;25(1):112. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01622-0. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40445450
-
Exploring resistance mechanisms and identifying QTLs for brown planthopper in tropical and subtropical rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm.Theor Appl Genet. 2025 Feb 20;138(3):49. doi: 10.1007/s00122-025-04839-6. Theor Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 39976729
References
-
- Godfray H.C., Beddington J.R., Crute I.R., Haddad L., Lawrence D., Muir J.F., Pretty J., Robinson S., Thomas S.M., Toulmin C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science. 2010;327:812–818. - PubMed
-
- Horgan F.G., Penalver Cruz A., Bernal C.C., Ramal A.F., Almazan M.L.P., Wilby A. Resistance and tolerance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), in rice infested at different growth stages across a gradient of nitrogen applications. Field Crops Res. 2018;217:53–65. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2017.12.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

