Microcystin-LR-Induced Interaction between M2 Tumor-Associated Macrophage and Colorectal Cancer Cell Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration through Regulating the Expression of TGF-β1 and CST3
- PMID: 37445705
- PMCID: PMC10341441
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310527
Microcystin-LR-Induced Interaction between M2 Tumor-Associated Macrophage and Colorectal Cancer Cell Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration through Regulating the Expression of TGF-β1 and CST3
Abstract
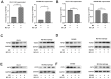
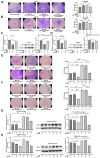
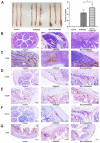
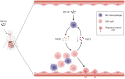
Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by cyanobacteria that has been demonstrated to promote colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the mechanism by which MC-LR enhances CRC in the tumor microenvironment (TME) is poorly understood. To elucidate its role in TME, a co-culture system was established using CRC cells and M2 macrophages in a Transwell chamber. The study found that MC-LR promotes CRC cell migration by upregulating TGF-β1 expression and secretion in M2 macrophages and downregulating CST3 in CRC cells. Neutralizing TGF-β1 increased CST3 expression in CRC cells, while overexpressing CST3 in CRC cells suppressed TGF-β1 expression in M2 macrophages, both of which weakened MC-LR-induced cellular motility in the co-culture system. In vivo, the mice in the MC-LR/AOM/DSS group had more tumor nodules, deeper tumor invasion, and higher M2 macrophage infiltration compared to the AOM/DSS group, and the expression of TGF-β1 and CST3 in tumors was consistent with the cellular level. Overall, this study provides insights into the regulatory mechanism of MC-LR on TME, revealing that MC-LR upregulates the expression and secretion of TGF-β1 in M2 macrophages, which in turn inhibits the expression of CST3 in CRC cells to promote migration.
Keywords: M2 tumor-associated macrophages; MC-LR; TGF-β1; colorectal cancer; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K.A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G.A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990;264:187–192. - PubMed
-
- Laureano-Rosario A.E., McFarland M., Bradshaw D.J., Metz J., Brewton R.A., Pitts T., Perricone C., Schreiber S., Stockley N., Wang G., et al. Dynamics of microcystins and saxitoxin in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida. Harmful Algae. 2021;103:102012. - PubMed
-
- Xu Q., Chen W., Gao G. Seasonal variations in microcystin concentrations in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008;145:75–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

