Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Hemostatic Applications: A Review of Recent Advances
- PMID: 37445718
- PMCID: PMC10342007
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310540
Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Hemostatic Applications: A Review of Recent Advances
Abstract
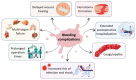
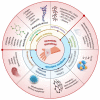
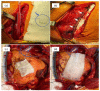
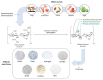
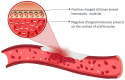
Hemorrhage is a detrimental event present in traumatic injury, surgery, and disorders of bleeding that can become life-threatening if not properly managed. Moreover, uncontrolled bleeding can complicate surgical interventions, altering the outcome of surgical procedures. Therefore, to reduce the risk of complications and decrease the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with hemorrhage, it is necessary to use an effective hemostatic agent that ensures the immediate control of bleeding. In recent years, there have been increasingly rapid advances in developing a novel generation of biomaterials with hemostatic properties. Nowadays, a wide array of topical hemostatic agents is available, including chitosan-based biomaterials that have shown outstanding properties such as antibacterial, antifungal, hemostatic, and analgesic activity in addition to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and wound-healing effects. This review provides an analysis of chitosan-based hemostatic biomaterials and discusses the progress made in their performance, mechanism of action, efficacy, cost, and safety in recent years.
Keywords: blood–material interaction; chitosan-based composites; hemostasis; topical hemostatic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chitosan-Based Composite Materials for Prospective Hemostatic Applications.Mar Drugs. 2018 Aug 4;16(8):273. doi: 10.3390/md16080273. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30081571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan-based hemostatic sponges as new generation hemostatic materials for uncontrolled bleeding emergency: Modification, composition, and applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2023 Jul 1;311:120780. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120780. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Carbohydr Polym. 2023. PMID: 37028883 Review.
-
Engineered Hemostatic Biomaterials for Sealing Wounds.Chem Rev. 2022 Aug 10;122(15):12864-12903. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c01015. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35731958 Review.
-
Chitosan-Based Hemostatic Hydrogels: The Concept, Mechanism, Application, and Prospects.Molecules. 2023 Feb 3;28(3):1473. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031473. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances of chitosan as a hemostatic material: Hemostatic mechanism, material design and prospective application.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Mar 1;327:121673. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121673. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 38171686 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Polyurethane Shape Memory Polymer Foam Dressings with Enhanced Blood and Cell Interactions for Improved Wound Healing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 May 7;17(18):26402-26415. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c02532. Epub 2025 Apr 22. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40261803 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Basil and Cinnamon Essential Oils on Bioactive Sponge Composites of Collagen Reinforced with Hydroxyapatite.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;18(3):626. doi: 10.3390/ma18030626. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942292 Free PMC article.
-
Porous Osteoplastic Composite Materials Based on Alginate-Pectin Complexes and Cation-Substituted Hydroxyapatites.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;17(13):1744. doi: 10.3390/polym17131744. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647755 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Biomaterial Surface Properties on Engineering Neural Tissue for Spinal Cord Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 4;24(17):13642. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713642. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686446 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan Hemostatic Dressings: Properties and Surgical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jun 22;16(13):1770. doi: 10.3390/polym16131770. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39000626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mohamed E., Fitzgerald A., Tsuzuki T. The Role of Nanoscale Structures in the Development of Topical Hemostatic Agents. Mater. Today Nano. 2021;16:100137. doi: 10.1016/j.mtnano.2021.100137. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

