Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Matrix Metalloproteinase 13 and the Analysis of the Specificity Loop and the S1'-Site
- PMID: 37445757
- PMCID: PMC10342107
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310577
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Matrix Metalloproteinase 13 and the Analysis of the Specificity Loop and the S1'-Site
Abstract
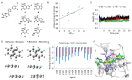
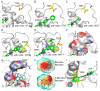
The specificity loop of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) is known to regulate recognition of their substrates, and the S1'-site surrounded by the loop is a unique place to address the selectivity of ligands toward each MMP. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of apo-MMP-13 and its complex forms with various ligands were conducted to identify the role of the specificity loop for the ligand binding to MMP-13. The MD simulations showed the dual role of T247 as a hydrogen bond donor to the ligand, as well as a contributor to the formation of the van der Waal surface area, with T245 and K249 on the S1'-site. The hydrophobic surface area mediated by T247 blocks the access of water molecules to the S1'-site of MMP-13 and stabilizes the ligand in the site. The F252 residue is flexible in order to search for the optimum location in the S1'-site of the apo-MMP-13, but once a ligand binds to the S1'-site, it can form offset π-π or edge-to-π stacking interactions with the ligand. Lastly, H222 and Y244 provide the offset π-π and π-CH(Cβ) interactions on each side of the phenyl ring of the ligand, and this sandwiched interaction could be critical for the ligand binding to MMP-13.
Keywords: MD simulations; S1′−site; matrix metalloproteinase 13; selective MMP inhibitors; specificity loop; π−CH(Cβ) interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Diaz-Canestro C., Puspitasari Y.M., Liberale L., Guzik T.J., Flammer A.J., Bonetti N.R., Wust P., Costantino S., Paneni F., Akhmedov A., et al. MMP-2 knockdown blunts age-dependent carotid stiffness by decreasing elastin degradation and augmenting eNOS activation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022;118:2385–2396. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab300. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

