Associations between Endothelial Lipase and Apolipoprotein B-Containing Lipoproteins Differ in Healthy Volunteers and Metabolic Syndrome Patients
- PMID: 37445857
- PMCID: PMC10341652
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310681
Associations between Endothelial Lipase and Apolipoprotein B-Containing Lipoproteins Differ in Healthy Volunteers and Metabolic Syndrome Patients
Abstract
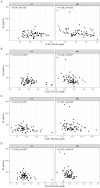
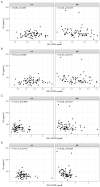
The association between serum levels of endothelial lipase (EL) and the serum levels and composition of apolipoprotein B (apoB)-containing lipoproteins in healthy subjects and patients with metabolic syndrome (MS) remained unexplored. Therefore, in the present study, we determined the serum levels and lipid content of apoB-containing lipoproteins using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and examined their association with EL serum levels in healthy volunteers (HVs) and MS patients. EL was significantly negatively correlated with the serum levels of cholesterol in large very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles, as well as with total-cholesterol-, free-cholesterol-, triglyceride-, and phospholipid-contents of VLDL and intermediate-density lipoprotein particles in MS patients but not in HVs. In contrast, EL serum levels were significantly positively correlated with the serum levels of apoB, triglycerides, and phospholipids in large low-density lipoprotein particles in HVs but not in MS patients. EL serum levels as well as the serum levels and lipid content of the majority of apoB-containing lipoprotein subclasses were markedly different in MS patients compared with HVs. We conclude that EL serum levels are associated with the serum levels and lipid content of apoB-containing lipoproteins and that these associations are markedly affected by MS.
Keywords: NMR spectroscopy; apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins; endothelial lipase; lipoprotein subclasses; metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between Endothelial Lipase, High-Density Lipoprotein, and Endothelial Function Differ in Healthy Volunteers and Metabolic Syndrome Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2073. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032073. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768410 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial lipase promotes the catabolism of ApoB-containing lipoproteins.Circ Res. 2004 Jun 25;94(12):1554-61. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000130657.00222.39. Epub 2004 Apr 29. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15117821
-
Effect of insulin therapy on metabolic fate of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in NIDDM.Diabetes. 1990 Sep;39(9):1017-27. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.9.1017. Diabetes. 1990. PMID: 2200727
-
Hepatic lipase deficiency.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1998 Dec;35(6):547-72. doi: 10.1080/10408369891234273. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1998. PMID: 9885775 Review.
-
Lipoprotein heterogeneity and apolipoprotein B metabolism.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997 Dec;17(12):3542-56. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.17.12.3542. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997. PMID: 9437204 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of the PCSK6 rs1531817(C/A) polymorphism with the prognosis and coronary stenosis in premature myocardial infarction patients: a prospective cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jul 22;23(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02206-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39039525 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Related Differences in the Associations between Adiponectin and Serum Lipoproteins in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Metabolic Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 1;12(9):1972. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12091972. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335486 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Levels of Adiponectin Are Strongly Associated with Lipoprotein Subclasses in Healthy Volunteers but Not in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 6;25(9):5050. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095050. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732266 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Oxidation Protein Products Are Strongly Associated with the Serum Levels and Lipid Contents of Lipoprotein Subclasses in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Metabolic Syndrome.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 11;13(3):339. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030339. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gauster M., Oskolkova O.V., Innerlohinger J., Glatter O., Knipping G., Frank S. Endothelial lipase-modified high-density lipoprotein exhibits diminished ability to mediate SR-BI (scavenger receptor B type I)-dependent free-cholesterol efflux. Pt 1Biochem. J. 2004;382:75–82. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031882. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schilcher I., Ledinski G., Radulovic S., Hallstrom S., Eichmann T., Madl T., Zhang F., Leitinger G., Kolb-Lenz D., Darnhofer B., et al. Endothelial lipase increases antioxidative capacity of high-density lipoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids. 2019;1864:1363–1374. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.06.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

