Prenatal SAMe Treatment Changes via Epigenetic Mechanism/s USVs in Young Mice and Hippocampal Monoamines Turnover at Adulthood in a Mouse Model of Social Hierarchy and Depression
- PMID: 37445911
- PMCID: PMC10361211
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310721
Prenatal SAMe Treatment Changes via Epigenetic Mechanism/s USVs in Young Mice and Hippocampal Monoamines Turnover at Adulthood in a Mouse Model of Social Hierarchy and Depression
Abstract
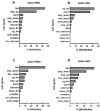
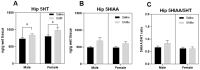
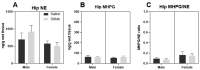
The role of hippocampal monoamines and their related genes in the etiology and pathogenesis of depression-like behavior, particularly in impaired sociability traits and the meaning of changes in USVs emitted by pups, remains unknown. We assessed the effects of prenatal administration of S-adenosyl-methionine (SAMe) in Sub mice that exhibit depressive-like behavior on serotonergic, dopaminergic and noradrenergic metabolism and the activity of related genes in the hippocampus (HPC) in adulthood in comparison to saline-treated control Sub mice. During postnatal days 4 and 8, we recorded and analyzed the stress-induced USVs emitted by the pups and tried to understand how the changes in the USVs' calls may be related to the changes in the monoamines and the activity of related genes. The recordings of the USVs showed that SAMe induced a reduction in the emitted flat and one-frequency step-up call numbers in PND4 pups, whereas step-down type calls were significantly increased by SAMe in PND8 pups. The reduction in the number of calls induced by SAMe following separation from the mothers implies a reduction in anxiety, which is an additional sign of decreased depressive-like behavior. Prenatal SAMe increased the concentrations of serotonin in the HPC in both male and female mice without any change in the levels of 5HIAA. It also decreased the level of the dopamine metabolite DOPAC in females. There were no changes in the levels of norepinephrine and metabolites. Several changes in the expression of genes associated with monoamine metabolism were also induced by prenatal SAMe. The molecular and biochemical data obtained from the HPC studies are generally in accordance with our previously obtained data from the prefrontal cortex of similarly treated Sub mice on postnatal day 90. The changes in both monoamines and their gene expression observed 2-3 months after SAMe treatment are associated with the previously recorded behavioral improvement and seem to demonstrate that SAMe is effective via an epigenetic mechanism.
Keywords: S-adenosyl-methionine; USVs; brain monoamine metabolism; depression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Prenatal SAMe Treatment Induces Changes in Brain Monoamines and in the Expression of Genes Related to Monoamine Metabolism in a Mouse Model of Social Hierarchy and Depression, Probably via an Epigenetic Mechanism.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 7;23(19):11898. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911898. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233200 Free PMC article.
-
S-Adenosyl-Methionine alleviates sociability aversion and reduces changes in gene expression in a mouse model of social hierarchy.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Jun 3;427:113866. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2022.113866. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35367299
-
Non-parametric analysis of neurochemical effects and Arc expression in amphetamine-induced 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalization.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Oct 1;312:174-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.042. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27288591
-
Evaluation of ultrasonic vocalizations in a neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia during the early life stages of rats.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Mar 1;146:28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.023. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30448422
-
[Neurobiology and pharmacotherapy of social phobia].Encephale. 2004 Jul-Aug;30(4):301-13. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95442-5. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15538306 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Animal Models of Autistic-like Behavior in Rodents: A Scoping Review and Call for a Comprehensive Scoring System.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 28;25(19):10469. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910469. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408797 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Assessing Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Mice: A Critical Review of Behavioral Tests and Methodological Considerations Searching to Improve Reliability.NeuroSci. 2025 Mar 27;6(2):27. doi: 10.3390/neurosci6020027. NeuroSci. 2025. PMID: 40265357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

