Multiple-Factors-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis Synoviocyte Activation Is Attenuated by the α2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonist Dexmedetomidine
- PMID: 37445932
- PMCID: PMC10341941
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310756
Multiple-Factors-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis Synoviocyte Activation Is Attenuated by the α2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonist Dexmedetomidine
Abstract
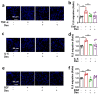
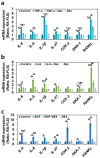
Dexmedetomidine (Dex) has analgesic and sedative properties and anti-inflammatory functions. Although the effects of Dex on arthritis have been revealed, the physiological mechanism underlying the interaction between Dex and rheumatoid arthritis (RA)-mediated inflammatory cytokines has not been fully studied. Inflamed and migrated fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) are involved in RA severity. Thus, we aimed to determine the effects of Dex on RA-FLSs treated with inflammatory cytokines and a growth factor as multiple stimulating inputs. TNF-α, IL-6, and EGF as multiple stimulating inputs increased the cAMP concentration of RA-FLSs, while Dex treatment reduced cAMP concentration. Dex reduced electroneutral sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter 1 (NBCn1) expression, NBC activity, and subsequent RA-FLS migration. The mRNA expression levels of RA-related factors, such as inflammatory cytokines and osteoclastogenesis factors, were enhanced by multiple-input treatment. Notably, Dex effectively reduced these expression levels in RA-FLSs. These results indicate that multiple inflammatory or stimulating inputs enhance RA-FLS migration, and treatment with Dex relieves activated RA-FLSs, suggesting that Dex is a potential therapeutic drug for RA.
Keywords: EGF; FLS; IL-6; TNF-α; dexmedetomidine; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CYLD suppression enhances the pro-inflammatory effects and hyperproliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by enhancing NF-κB activation.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Oct 3;20(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1722-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30285829 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic synovial fibroblasts are modulated by NBCn1 as a potential target in rheumatoid arthritis.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Apr;54(4):503-517. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00756-6. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35414711 Free PMC article.
-
IL-37 alleviates TNF-α-induced pyroptosis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by inhibiting the NF-κB/GSDMD signaling pathway.Immunobiology. 2023 May;228(3):152382. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2023.152382. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Immunobiology. 2023. PMID: 37075579
-
Glycogen Metabolism and Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Glycogen Synthase 1 in Regulation of Synovial Inflammation via Blocking AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activation.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 27;9:1714. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01714. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30100905 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Phytochemical, DIM, Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and TNF-α Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Production of Synovial Fibroblasts From Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients by Targeting MAPK and AKT/mTOR Signal Pathway.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 23;10:1620. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01620. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31396207 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of Dexmedetomidine on Analgesia and Inflammatory Response in Knee Surgery: A Study of IPACK and ACB Techniques.Med Sci Monit. 2025 May 11;31:e947087. doi: 10.12659/MSM.947087. Med Sci Monit. 2025. PMID: 40384422 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Schendrigin I.N., Timchenko L.D., Rzhepakovsky I.V., Avanesyan S.S., Sizonenko M.N., Grimm W.D., Povetkin S.N., Piskov S.I. Clinical and Pathogenetic Significance of Amylase Level and Microtomographic Index of Synovial Fluid in Various Joint Lesions. Sovrem. Tehnol. Med. 2022;14:42–49. doi: 10.17691/stm2022.14.6.05. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

