Unraveling the Roles of miR-204-5p and HMGA2 in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 37445942
- PMCID: PMC10341554
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310764
Unraveling the Roles of miR-204-5p and HMGA2 in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Tumorigenesis
Abstract
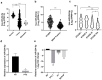
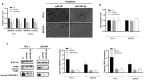
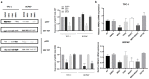
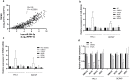
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine malignant tumor with an increasing incidence rate. Although differentiated types of thyroid cancer generally present good clinical outcomes, some dedifferentiate into aggressive and lethal forms. However, the molecular mechanisms governing aggressiveness and dedifferentiation are still poorly understood. Aberrant expression of miRNAs is often correlated to tumor development, and miR-204-5p has previously been identified in papillary thyroid carcinoma as downregulated and associated with aggressiveness. This study aimed to explore its role in thyroid tumorigenesis. To address this, gain-of-function experiments were performed by transiently transfecting miR-204-5p in thyroid cancer cell lines. Then, the clinical relevance of our data was evaluated in vivo. We prove that this miRNA inhibits cell invasion by regulating several targets associated with an epithelial-mesenchymal transition, such as SNAI2, TGFBR2, SOX4 and HMGA2. HMGA2 expression is regulated by the MAPK pathway but not by the PI3K, IGF1R or TGFβ pathways, and the inhibition of cell invasion by miR-204-5p involves direct binding and repression of HMGA2. Finally, we confirmed in vivo the relationship between miR-204-5p and HMGA2 in human PTC and a corresponding mouse model. Our data suggest that HMGA2 inhibition offers promising perspectives for thyroid cancer treatment.
Keywords: EMT; HMGA2; MAPK; miR-204-5p; microRNAs; papillary thyroid carcinoma; thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
HMGA2 Overexpression in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Promotes Thyroid Cell Dedifferentiation and Invasion, and These Effects Are Counteracted by Suramin.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 14;26(4):1643. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041643. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004107 Free PMC article.
-
miR-98-5p promotes apoptosis and inhibits migration and cell growth in papillary thyroid carcinoma through Bax/Caspase-3 by HMGA2.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Feb;34(2):e23044. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23044. Epub 2019 Oct 31. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31670857 Free PMC article.
-
miR-199b-5p-Stonin 2 axis regulates metastases and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of papillary thyroid carcinoma.IUBMB Life. 2019 Jan;71(1):28-40. doi: 10.1002/iub.1889. Epub 2018 Oct 16. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 30325582
-
MicroRNA Deregulation in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Biology.Int J Endocrinol. 2014;2014:743450. doi: 10.1155/2014/743450. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Int J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25202329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of TGFβ signaling and microRNA in thyroid cell loss of differentiation and cancer progression.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Sep 2;63(5):536-544. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000172. eCollection 2019. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31482959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HMGA2 promotes cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 1;14:1320887. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1320887. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38361784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing of LncRNA XIST Suppressed Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma by Modulating miR-204/FN1 Axis.ACS Omega. 2025 May 6;10(19):19643-19654. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00390. eCollection 2025 May 20. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40415854 Free PMC article.
-
HMGA2 Overexpression in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Promotes Thyroid Cell Dedifferentiation and Invasion, and These Effects Are Counteracted by Suramin.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 14;26(4):1643. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041643. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004107 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory network of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated non-coding RNAs in thyroid cancer: molecular mechanisms, clinical implications, and therapeutic strategies.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 2;15:1592467. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1592467. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40530008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding high mobility group A2 protein expression regulation and implications in human cancers.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jul 31;15(1):322. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01202-x. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39085703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

