Intra-Articular Lactate Dehydrogenase A Inhibitor Oxamate Reduces Experimental Osteoarthritis and Nociception in Rats via Possible Alteration of Glycolysis-Related Protein Expression in Cartilage Tissue
- PMID: 37445948
- PMCID: PMC10341729
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310770
Intra-Articular Lactate Dehydrogenase A Inhibitor Oxamate Reduces Experimental Osteoarthritis and Nociception in Rats via Possible Alteration of Glycolysis-Related Protein Expression in Cartilage Tissue
Abstract
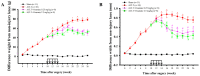
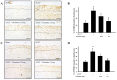
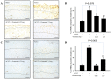
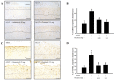
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis and joint disorder worldwide. Metabolic reprogramming of osteoarthritic chondrocytes from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis results in the accumulation of lactate from glycolytic metabolite pyruvate by lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), leading to cartilage degeneration. In the present study, we investigated the protective effects of the intra-articular administration of oxamate (LDHA inhibitor) against OA development and glycolysis-related protein expression in experimental OA rats. The animals were randomly allocated into four groups: Sham, anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT), ACLT + oxamate (0.25 and 2.5 mg/kg). Oxamate-treated groups received an intra-articular injection of oxamate once a week for 5 weeks. Intra-articular oxamate significantly reduced the weight-bearing defects and knee width in ACLT rats. Histopathological analyses showed that oxamate caused significantly less cartilage degeneration in the ACLT rats. Oxamate exerts hypertrophic effects in articular cartilage chondrocytes by inhibiting glucose transporter 1, glucose transporter 3, hexokinase II, pyruvate kinase M2, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases 1 and 2, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2, and LHDA. Further analysis revealed that oxamate significantly reduced chondrocyte apoptosis in articular cartilage. Oxamate attenuates nociception, inflammation, cartilage degradation, and chondrocyte apoptosis and possibly attenuates glycolysis-related protein expression in ACLT-induced OA rats. The present findings will facilitate future research on LDHA inhibitors in prevention strategies for OA progression.
Keywords: chondrocytes; glycolysis; lactate dehydrogenase A; osteoarthritis; oxamate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

