Durvillaea antarctica: A Seaweed for Enhancing Immune and Cardiometabolic Health and Gut Microbiota Composition Modulation
- PMID: 37445955
- PMCID: PMC10341711
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310779
Durvillaea antarctica: A Seaweed for Enhancing Immune and Cardiometabolic Health and Gut Microbiota Composition Modulation
Abstract
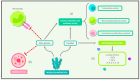
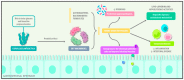
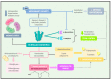
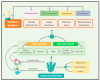
Durvillaea antarctica is the seaweed that is the most consumed by the Chilean population. It is recognized worldwide for its high nutritional value in protein, vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. This is a narrative review in which an extensive search of the literature was performed to establish the immunomodulator, cardiometabolic, and gut microbiota composition modulation effect of Durvillaea antarctica. Several studies have shown the potential of Durvillaea antarctica to function as prebiotics and to positively modulate the gut microbiota, which is related to anti-obesity, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, lipid-lowering, and hypoglycemic effects. The quantity of Bacteroides was negatively correlated with that of inflammatory monocytes and positively correlated with the levels of several gut metabolites. Seaweed-derived polysaccharides modulate the quantity and diversity of beneficial intestinal microbiota, decreasing phenol and p-cresol, which are related to intestinal diseases and the loss of intestinal function. Additionally, a beneficial metabolic effect related to this seaweed was observed, mainly promoting the decrease in the glycemic levels, lower cholesterol levels and cardiovascular risk. Consuming Durvillaea antarctica has a positive impact on the immune system, and its bioactive compounds provide beneficial effects on glycemic control and other metabolic parameters.
Keywords: Durvillaea antarctica; cardiovascular risk; metabolic syndrome; microbiota; seaweed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ortiz J., Romero N., Robert P., Araya J., Lopez-Hernández J., Bozzo C., Navarrete E., Osorio A., Rios A. Dietary Fiber, Amino Acid, Fatty Acid and Tocopherol Contents of the Edible Seaweeds Ulva Lactuca and Durvillaea Antarctica. Food Chem. 2006;99:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.027. - DOI
-
- Margozzini Maira P., Passi Solar A. Encuesta Nacional de Salud, ENS 2016-2017: Un aporte a la planificación sanitaria y políticas públicas en Chile. ARS Med. 2018;43:30–34. doi: 10.11565/arsmed.v43i1.1354. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

