Molecular Dynamics Simulations Combined with Markov Model to Explore the Effect of Allosteric Inhibitor Binding on Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4
- PMID: 37446009
- PMCID: PMC10342045
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310831
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Combined with Markov Model to Explore the Effect of Allosteric Inhibitor Binding on Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4
Abstract
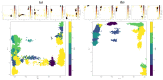
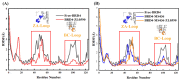
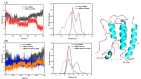
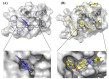
Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4 (BRD4) can play an important role in gene transcriptional regulation of tumor development and survival by participating in histone modification epigenetic mechanism. Although it has been reported that novel allosteric inhibitors such as ZL0590 have a high affinity with target protein BRD4 and good efficacy, their inhibitory mechanism has not been studied further. The aim of this study was to reveal the inhibition mechanism of allosteric inhibitor ZL0590 on Free-BRD4 and BRD4 binding MS436 (orthosteric inhibitor) by molecular dynamics simulation combined with a Markov model. Our results showed that BRD4-ZL0590 led to α-helices formation of 100-105 compared with Free-BRD4; the combination of MS436 caused residues 30-40 and 95-105 to form α-helices, while the combination of allosteric inhibitors untangled the α-helices formed by the MS436. The results of Markov flux analysis showed that the binding process of inhibitors mainly involved changes in the degree of α-helices at ZA loop. The binding of ZL0590 reduced the distance between ZA loop and BC loop, blocked the conformation at the active site, and inhibited the binding of MS436. After the allosteric inhibitor binding, the MS436 that could normally penetrate into the interior of the pocket was floating on the edge of the active pocket and did not continue to penetrate into the active pocket as expected. In summary, we provide a theoretical basis for the inhibition mechanism of ZL0590 against BRD4, which can be used as a reference for improving the development of drug targets for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4 (BRD4); Markov model; allosteric regulation; conformational changes; molecular dynamics simulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Unveiling Allosteric Regulation and Binding Mechanism of BRD9 through Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Markov Modeling.Molecules. 2024 Jul 25;29(15):3496. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153496. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39124901 Free PMC article.
-
Binding Mechanism of Inhibitors to BRD4 and BRD9 Decoded by Multiple Independent Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Deep Learning.Molecules. 2024 Apr 19;29(8):1857. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081857. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675678 Free PMC article.
-
Pyronaridine as a Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4-N-Terminal Bromodomain (BRD4-BD1) Inhibitor: In Silico Database Mining, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Molecules. 2023 Jul 28;28(15):5713. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155713. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570684 Free PMC article.
-
Privileged Scaffolds Targeting Bromodomain-containing Protein 4.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(7):600-627. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220209143949. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35139799 Review.
-
A patent review of BRD4 inhibitors (2013-2019).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020 Jan;30(1):57-81. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2020.1702645. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020. PMID: 31815566 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling Allosteric Regulation and Binding Mechanism of BRD9 through Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Markov Modeling.Molecules. 2024 Jul 25;29(15):3496. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153496. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39124901 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

