Discovery and Mechanism of Novel 7-Aliphatic Amine Tryptanthrin Derivatives against Phytopathogenic Bacteria
- PMID: 37446077
- PMCID: PMC10341529
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310900
Discovery and Mechanism of Novel 7-Aliphatic Amine Tryptanthrin Derivatives against Phytopathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
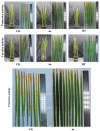
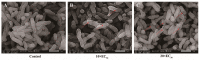
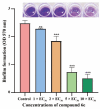
Rice bacterial leaf blight is a destructive bacterial disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) that seriously threatens crop yields and their associated economic benefits. In this study, a series of improved dissolubility 7-aliphatic amine tryptanthrin derivatives was designed and synthesized, and their potency in antibacterial applications was investigated. Notably, compound 6e exhibited excellent activity against Xoo, with an EC50 value of 2.55 μg/mL, compared with the positive control bismerthiazol (EC50 = 35.0 μg/mL) and thiodiazole copper (EC50 = 79.4 μg/mL). In vivo assays demonstrated that 6e exhibited a significant protective effect on rice leaves. After exposure, the morphology of the bacteria was partially atrophied by SEM. Furthermore, 6e increased the accumulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species, causing cell apoptosis and the formation of bacterial biofilms. All the results indicated that 6e could be a potential agrochemical bactericide for controlling phytopathogenic bacteria.
Keywords: 7-aliphatic amine tryptanthrin derivatives; SEM; Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design, Synthesis, and Mechanism of Novel 9-Aliphatic Amine Tryptanthrin Derivatives against Phytopathogenic Bacteria.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Oct 4;71(39):14232-14242. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c03738. Epub 2023 Sep 25. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37749804
-
Synthesis and Antibacterial Evaluation of Novel 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives Containing Sulfonate/Carboxylate Moiety.Molecules. 2020 Mar 25;25(7):1488. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071488. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32218317 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives Containing a Cinnamic Acid Moiety as Potential Bactericide for Rice Bacterial Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 26;20(5):1020. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051020. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30813628 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New Sulfone Derivatives Containing a 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Moiety as Active Antibacterial Agents.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Mar 28;66(12):3093-3100. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b06061. Epub 2018 Mar 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29502398
-
[Production and biological activity of the triazine derivatives: focusing on antibiotics produced by bacteria].Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2025;80(1):1-13. doi: 10.3412/jsb.80.1. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2025. PMID: 40044155 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Recent advances of tryptanthrin and its derivatives as potential anticancer agents.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Jan 4;15(4):1127-1147. doi: 10.1039/d3md00698k. eCollection 2024 Apr 24. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38665827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jiang N., Yan J., Liang Y., Shi Y.L., He Z.Z., Wu Y.T., Zeng Q., Liu X.L., Peng J.H. Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review. Rice. 2020;13:3. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

