Structural Modifications Introduced by NS2B Cofactor Binding to the NS3 Protease of the Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus
- PMID: 37446083
- PMCID: PMC10342073
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310907
Structural Modifications Introduced by NS2B Cofactor Binding to the NS3 Protease of the Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus
Abstract
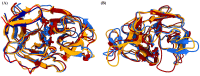
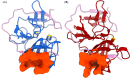
Kyasanur Forest Disease virus (KFDV), a neglected human pathogenic virus, is a Flavivirus that causes severe hemorrhagic fever in humans. KFDV is transmitted to humans by the bite of the hard tick (Haemaphysalis spinigera), which acts as a reservoir of KFDV. The recent expansion of the endemic area of KFDV is of concern and requires the development of new preventive measures against KFDV. Currently, there is no antiviral therapy against KFDV, and the existing vaccine has limited efficacy. To develop a new antiviral therapy against KFDV, we focused on the nonstructural proteins NS2B and NS3 of KFDV, which are responsible for serine protease activity. Viral proteases have shown to be suitable therapeutic targets in the development of antiviral drugs against many diseases. However, success has been limited in flaviviruses, mainly because of the important features of the active site, which is flat and highly charged. In this context, the present study focuses on the dynamics of NS2B and NS3 to identify potential allosteric sites in the NS2B/NS3 protease of KDFV. To our knowledge, there are no reports on the dynamics of NS2B and NS3 in KFDV, and the crystal structure of the NS2B/NS3 protease of KFDV has not yet been solved. Overall, we created the structure of the NS2B/NS3 protease of KFDV using AlphaFold and performed molecular dynamics simulations with and without NS2B cofactor to investigate structural rearrangements due to cofactor binding and to identify alternative allosteric sites. The identified allosteric site is promising due to its geometric and physicochemical properties and druggability and can be used for new drug development. The applicability of the proposed allosteric binding sites was verified for the best-hit molecules from the virtual screening and MD simulations.
Keywords: AlphaFold; KFDV; MD; NS2B; NS3; PCA; allosteric binding site; clustering; conformational change.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Work T.H., Trapido H. Summary of Preliminary Report of Investigations of the Virus Research Centre on an Epidemic Disease Affecting Forest Villagers and Wild Monkeys of Shimoga District, Mysore. Indian J. Med. Sci. 1957;11:341–342. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt P.N., Work T.H., Varma M.G., Trapido H., Murthy D.P., Rodrigues F.M. Kyasanur Forest Diseases. IV. Isolation of Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus from Infected Humans and Monkeys of Shimogadistrict, Mysore State. Indian J. Med. Sci. 1996;20:316–320. - PubMed
-
- Dhaka R., Verma R., Kumar R., Dhankar M., Bhalla K., Agrawal G. Kyasanur Forest Disease: A Rare Viral Hemorrhagic Disease in India. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health. 2018;5:3149–3151. doi: 10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20183042. - DOI
-
- Trapido H., Rajagopalan P.K., Work T.H., Varma M G Kyasanur Forest Disease VIII. Isolation of Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus from Naturally Infected Ticks of the Genus Haemaphysalis. Indian J. Med. Res. 1959;47:133–138. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

