Experimental Insights into the Interplay between Histone Modifiers and p53 in Regulating Gene Expression
- PMID: 37446210
- PMCID: PMC10342072
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241311032
Experimental Insights into the Interplay between Histone Modifiers and p53 in Regulating Gene Expression
Abstract
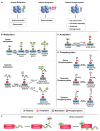
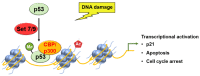
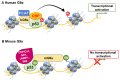
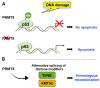
Chromatin structure plays a fundamental role in regulating gene expression, with histone modifiers shaping the structure of chromatin by adding or removing chemical changes to histone proteins. The p53 transcription factor controls gene expression, binds target genes, and regulates their activity. While p53 has been extensively studied in cancer research, specifically in relation to fundamental cellular processes, including gene transcription, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression, its association with histone modifiers has received limited attention. This review explores the interplay between histone modifiers and p53 in regulating gene expression. We discuss how histone modifications can influence how p53 binds to target genes and how this interplay can be disrupted in cancer cells. This review provides insights into the complex mechanisms underlying gene regulation and their implications for potential cancer therapy.
Keywords: cancer; chromatin structure; gene regulation; histone modifications; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Disparate chromatin landscapes and kinetics of inactivation impact differential regulation of p53 target genes.Cell Cycle. 2010 Sep 1;9(17):3428-37. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.17.12998. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20818159 Free PMC article.
-
RAD6 regulates the dosage of p53 by a combination of transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;32(2):576-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05966-11. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22083959 Free PMC article.
-
Readout of histone methylation by Trim24 locally restricts chromatin opening by p53.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Jul;30(7):948-957. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01021-8. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37386214 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying Chromatin by Histone Tail Clipping.J Mol Biol. 2018 Sep 14;430(18 Pt B):3051-3067. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.07.013. Epub 2018 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30009770 Review.
-
The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell fate.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Apr;20(4):199-210. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0110-x. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30824861 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrical Stimulation Generates Induced Tumor-Suppressing Cells, Offering a Potential Option for Combatting Breast Cancer and Bone Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 25;26(3):1030. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031030. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940798 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of rumen-protected lysine on antler growth performance, fecal bacterial community, and blood gene expression in sika deer.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 11;12:1583605. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1583605. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40717913 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of p53 Mutations in Early and Late Response to Mitotic Aberrations.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 8;15(2):244. doi: 10.3390/biom15020244. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Proteomics Analysis Unravels the Molecular Signatures of Tonsillar B Cells in PFAPA and OSAS in the Pediatric Population.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 10;26(14):6621. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146621. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724870 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

