Fabrication and Characterization of Polylactic Acid Electrospun Wound Dressing Modified with Polyethylene Glycol, Rosmarinic Acid and Graphite Oxide
- PMID: 37446516
- PMCID: PMC10343514
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13132000
Fabrication and Characterization of Polylactic Acid Electrospun Wound Dressing Modified with Polyethylene Glycol, Rosmarinic Acid and Graphite Oxide
Abstract
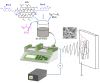
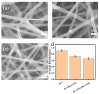
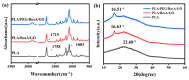
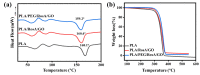
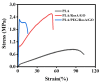
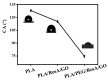
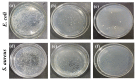
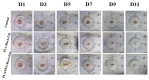
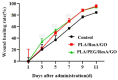
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a biodegradable polymer made from natural sources, and its electrospinning (e-spinning) nanofiber membrane doped with antibacterial ingredients is widely used in the field of medical dressings. In this research, 9 wt% of rosmarinic acid (RosA) and 0.04 wt% of graphite oxide (GO) with synergistic antibacterial activity were introduced into the e-spinning PLA precursor solution, and the obtained PLA nanofiber membrane showed good antibacterial properties and wound healing effects. At the same time, a nonionic amphiphilic polymer, polyethylene glycol (PEG), was also introduced into this system to improve the hydrophilicity of the e-spinning membrane for wound healing application. The morphological characterization showed the RosA/GO and PEG did not affect the e-spinning of PLA. The tests of mechanical performance and wettability demonstrated that PEG and RosA/GO incorporated in PLA have migrated easily to the surface of the fiber. The e-spun PLA/PEG/RosA/GO membrane showed good antibacterial activity and promoted initial wound healing quickly, which would be a promising application in wound dressing.
Keywords: PLA nanofiber; electrospinning; rosmarinic acid; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kim B.S., Kwon Y.W., Kong J.S., Park G.T., Gao G., Han W., Kim M.B., Lee H., Kim J.H., Cho D.W. 3D cell printing of in vitro stabilized skin model and in vivo pre-vascularized skin patch using tissue-specific extracellular matrix bioink: A step towards advanced skin tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2018;168:38–53. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.03.040. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haalboom M., Blokhuis-Arkes M.H.E., Beuk R., Meerwaldt R.J., Klont R., Schijffelen M.J., Bowler P.B., Burnet M., Sigl E., Van Der Palen J.A.M. Culture results from wound biopsy versus wound swab: Does it matter for the assessment of wound infection? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019;25:629.e7–629.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.08.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

