Perovskite-Based X-ray Detectors
- PMID: 37446540
- PMCID: PMC10343290
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13132024
Perovskite-Based X-ray Detectors
Abstract
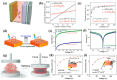
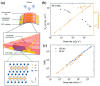
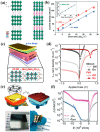
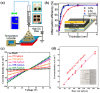
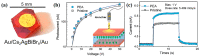
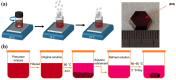
X-ray detection has widespread applications in medical diagnosis, non-destructive industrial radiography and safety inspection, and especially, medical diagnosis realized by medical X-ray detectors is presenting an increasing demand. Perovskite materials are excellent candidates for high-energy radiation detection based on their promising material properties such as excellent carrier transport capability and high effective atomic number. In this review paper, we introduce X-ray detectors using all kinds of halide perovskite materials along with various crystal structures and discuss their device performance in detail. Single-crystal perovskite was first fabricated as an active material for X-ray detectors, having excellent performance under X-ray illumination due to its superior photoelectric properties of X-ray attenuation with μm thickness. The X-ray detector based on inorganic perovskite shows good environmental stability and high X-ray sensitivity. Owing to anisotropic carrier transport capability, two-dimensional layered perovskites with a preferred orientation parallel to the substrate can effectively suppress the dark current of the device despite poor light response to X-rays, resulting in lower sensitivity for the device. Double perovskite applied for X-ray detectors shows better attenuation of X-rays due to the introduction of high-atomic-numbered elements. Additionally, its stable crystal structure can effectively lower the dark current of X-ray detectors. Environmentally friendly lead-free perovskite exhibits potential application in X-ray detectors by virtue of its high attenuation of X-rays. In the last section, we specifically introduce the up-scaling process technology for fabricating large-area and thick perovskite films for X-ray detectors, which is critical for the commercialization and mass production of perovskite-based X-ray detectors.
Keywords: X-ray detector; double perovskite; inorganic perovskite; lead-free perovskite; perovskite; photoelectronic effect; two-dimensional layered perovskite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hoheisel M. Review of medical imaging with emphasis on X-ray detectors. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2006;563:215–224. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2006.01.123. - DOI
-
- Zhou Y., Chen J., Bakr O.M., Mohammed O.F. Metal Halide Perovskites for X-ray Imaging Scintillators and Detectors. ACS Energy Lett. 2021;6:739–768. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c02430. - DOI
-
- Nikl M., Yoshikawa A. Recent R&D Trends in Inorganic Single-Crystal Scintillator Materials for Radiation Detection. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015;3:463–481.
-
- Weber M.J. Inorganic scintillators: Today and tomorrow. J. Lumin. 2002;100:35–45. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2313(02)00423-4. - DOI
-
- Maddalena F., Xie A., Arramel, Witkowski M.E., Makowski M., Mahler B., Drozdowski W., Mariyappan T., Springham S.V., Coquet P., et al. Effect of commensurate lithium doping on the scintillation of two-dimensional perovskite crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2021;9:2504–2512. doi: 10.1039/D0TC05647B. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

