Protective Effect of Astragaloside IV against Cadmium-Induced Damage on Mouse Renal Podocytes (MPC5)
- PMID: 37446560
- PMCID: PMC10343813
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28134897
Protective Effect of Astragaloside IV against Cadmium-Induced Damage on Mouse Renal Podocytes (MPC5)
Abstract
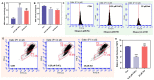
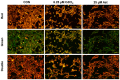
In this study, we investigated the protective effect of Astragaloside IV (Ast) on mouse podocytes and its possible mechanism of action by constructing a cadmium-induced mouse renal podocytes model. We investigated the effects of cadmium (Cd) toxicity on cell number, morphology, the mitochondrial status of subcellular organelles, protein and gene levels, and the protective effects of Ast by constructing a model of Cd-induced damage to mouse renal podocytes (MPC5) and giving Ast protection at the same time. The results showed that exposure of MPC5 cells to CdCl2 culture medium containing 6.25 μM concentration acted with low cell mortality, but the mortality of MPC5 cells increased with the prolongation of cadmium exposure time. Given Ast, the death rate in the low dose group (12.5 μM) was significantly reduced, while the death rate in the medium dose group (25 μM) was extremely significantly reduced. In comparison to the control group, the Cd-exposed group exhibited a significant increase of 166.7% in malondialdehyde (MDA) content and a significant decrease of 17.1% in SOD activity. The mitochondrial membrane potential was also reduced to varying degrees. However, in the Ast-protected group compared to the Cd-exposed group, the MDA content significantly decreased by 20.8%, the SOD activity decreased by 7.14%, and the mitochondrial membrane potential showed a significant increase. Fluorescence staining of mitochondrial membrane potential indicated that Cd exposure caused mitochondrial apoptosis. In the 12-h cadmium-exposed group, the protein expression of Nephrin in mice significantly decreased by 33.4%. However, the expression of the Desmin protein significantly increased by 67.8%, and the expression of the autophagy protein LC3-II significantly increased by 55.5%. Meanwhile, the expression of PINK1, a mitochondrial autophagy pathway protein, was significantly increased in the 12 h and 24 h cadmium exposure groups. The mRNA level of PINK1 was significantly increased, and that of Parkin was decreased in the 48 h cadmium exposure group. Compared to the Cd-exposed group, the Ast group showed more significant improvements in the expression of podocyte structure, functional proteins, and mitochondrial autophagy pathway proteins. The immunological assay of mitochondrial autophagic pathway proteins further indicated that Cd-induced damage to MPC5 cells might be associated with the dysregulation of mitochondrial autophagy.
Keywords: Astragaloside IV; MPC5; cadmium; diabetic nephropathy; mitochondria; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Yiqi Yangyin Huazhuo Tongluo Formula alleviates diabetic podocyte injury by regulating miR-21a-5p/FoxO1/PINK1-mediated mitochondrial autophagy.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Jan 20;45(1):27-34. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.04. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 39819709 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Wogonin protects glomerular podocytes by targeting Bcl-2-mediated autophagy and apoptosis in diabetic kidney disease.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Jan;43(1):96-110. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00721-5. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 34253875 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc42 upregulation under high glucose induces podocyte apoptosis and impairs β-cell insulin secretion.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 10;13:905703. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.905703. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36034435 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of astragalosides from Radix Astragali on adriamycin-induced podocyte injury.Exp Ther Med. 2018 May;15(5):4485-4490. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5933. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29731833 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Oxidative Stress-Induced Autophagy by Cadmium Exposure in Kidney, Liver, and Bone Damage, and Neurotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13491. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113491. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362277 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021YFD1600400/National Key Research and Development Program
- 2020GY-236/General Plan of Shaanxi Province
- 2022NY-035/General Plan of Shaanxi Province
- 2021ZDLNY04-01/Key Industrial Chain Projects of the Shaanxi Province-Agricultural Field
- 2022ZDLNY04-05/Key Industrial Chain Projects of the Shaanxi Province-Agricultural Field
- 22JC021/projects of the Education Department of Shaanxi Province
- 202131/Project from Weiyang Technology Bureau
- 21NYYF0022/Project from the Xi'an City Innovation Plan-Agricultural Field
- 2022SLZDCY-006/11 key industrial chain projects from Yanan science and technology bureau
- S2022-ZC-QCYK-0011/project from Qinchuang Yuan "Scientist& Engineers" Team
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

