Combination of Lycopene and Curcumin Synergistically Alleviates Testosterone-Propionate-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Sprague Dawley Rats via Modulating Inflammation and Proliferation
- PMID: 37446563
- PMCID: PMC10343798
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28134900
Combination of Lycopene and Curcumin Synergistically Alleviates Testosterone-Propionate-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Sprague Dawley Rats via Modulating Inflammation and Proliferation
Abstract
Background: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a progressive urological disease occurring in middle-aged and elderly men, which can be characterized by the non-malignant overgrowth of stromal and epithelial cells in the transition zone of the prostate. Previous studies have demonstrated that lycopene can inhibit proliferation, while curcumin can strongly inhibit inflammation. This study aims to determine the inhibitory effect of the combination of lycopene and curcumin on BPH.
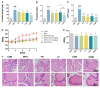
Method: To induce BPH models in vitro and in vivo, the BPH-1 cell line and Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were used, respectively. Rats were divided into six groups and treated daily with a vehicle, lycopene (12.5 mg/kg), curcumin (2.4 mg/kg), a combination of lycopene and curcumin (12.5 mg/kg + 2.4 mg/kg) or finasteride (5 mg/kg). Histologic sections were examined via hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemistry. Hormone and inflammatory indicators were detected via ELISA. Network pharmacology analysis was used to fully predict the therapeutic mechanism of the combination of lycopene and curcumin on BPH.
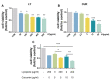
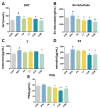
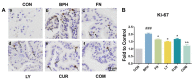
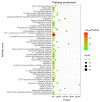
Results: Combination treatment significantly attenuated prostate hyperplasia, alleviated BPH pathological features and decreased the expression of Ki-67 in rats. The upregulation of the expression of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), 5α-reductase, estradiol (E2) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in BPH rats was significantly blocked by the combination treatment. The expression levels of inflammatory factors including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α were strongly inhibited by the combination treatment. From the network pharmacology analysis, it was found that the main targets for inhibiting BPH are AKT1, TNF, EGFR, STAT3 and PTGS2, which are enriched in pathways in cancer.
Conclusion: The lycopene and curcumin combination is a potential and more effective agent to prevent or treat BPH.
Keywords: BPH; curcumin; inflammation; lycopene; synergistic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
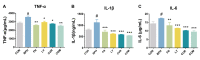

References
-
- El-Sherbiny M., El-Shafey M., El-Agawy M.S.E.-d., Mohamed A.S., Eisa N.H., Elsherbiny N.M. Diacerein ameliorates testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats: Effect on oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108082. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108082. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang W., Cao G., Sun Y., Wu F., Wang Q., Xu T., Hu H., Xu K. Depressive symptoms in individuals diagnosed with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia (LUTS/BPH) in middle-aged and older Chinese individuals: Results from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2022;296:660–666. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.09.045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rachael N., Dianna M.E.B. Patient-Friendly Summary of the ACR Appropriateness Criteria: Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms-Suspicion of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2022;19:e9. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Aziz A.M., El-Tahawy N.F.G., Abdel haleem M.A.S., Mohammed M.M., Ali A.I., Ibrahim Y.F. Amelioration of testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia using febuxostat in rats: The role of VEGF/TGFβ and iNOS/COX-2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020;889:173631. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173631. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

