Evaluation of the Possible Pathways Involved in the Protective Effects of Quercetin, Naringenin, and Rutin at the Gene, Protein and miRNA Levels Using In-Silico Multidimensional Data Analysis
- PMID: 37446564
- PMCID: PMC10343678
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28134904
Evaluation of the Possible Pathways Involved in the Protective Effects of Quercetin, Naringenin, and Rutin at the Gene, Protein and miRNA Levels Using In-Silico Multidimensional Data Analysis
Abstract
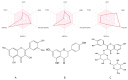
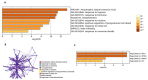
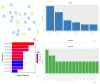
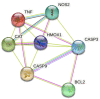
Flavonoids are secondary metabolites that are non-essential for plant growth or survival, and they also provide numerous health benefits to humans. They are antioxidants that shield plants from the ill effects of ultraviolet light, pests, and diseases. They are beneficial to health for several reasons, including lowering inflammation, boosting cardiovascular health, and lowering cancer risk. This study looked into the physicochemical features of these substances to determine the potential pharmacological pathways involved in their protective actions. Potential targets responsible for the protective effects of quercetin, naringenin, and rutin were identified with SwissADME. The associated biological processes and protein-protein networks were analyzed by using the GeneMANIA, Metascape, and STRING servers. All the flavonoids were predicted to be orally bioavailable, with more than 90% targets as enzymes, including kinases and lyases, and with common targets such as NOS2, CASP3, CASP9, CAT, BCL2, TNF, and HMOX1. TNF was shown to be a major target in over 250 interactions. To extract the "biological meanings" from the MCODE networks' constituent parts, a GO enrichment analysis was performed on each one. The most important transcription factors in gene regulation were RELA, NFKB1, PPARG, and SP1. Treatment with quercetin, naringenin, or rutin increased the expression and interaction of the microRNAs' hsa-miR-34a-5p, hsa-miR-30b-5p, hsa-let-7a-5p, and hsa-miR-26a-1-3p. The anticancer effects of hsa-miR-34a-5p have been experimentally confirmed. It also plays a critical role in controlling other cancer-related processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, EMT, and metastasis. This study's findings might lead to a deeper comprehension of the mechanisms responsible for flavonoids' protective effects and could present new avenues for exploration.
Keywords: computational analysis; flavonoids; gene interactions; miRNAs; pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA profiling reveals dysregulated microRNAs and their target gene regulatory networks in cemento-ossifying fibroma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2018 Jan;47(1):78-85. doi: 10.1111/jop.12650. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018. PMID: 29032608
-
Neurotherapeutic Effects of Quercetin and Its Metabolite Compounds on Cognitive Impairment and Parkinson's Disease: An In Silico Study.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2023 Mar;48(2):151-169. doi: 10.1007/s13318-023-00816-w. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2023. PMID: 36848007
-
Investigation of key miRNAs and target genes in bladder cancer using miRNA profiling and bioinformatic tools.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Dec;41(12):8127-35. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3713-5. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25189652
-
MicroRNA expression in male infertility.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2022 Jul;34(12):805-818. doi: 10.1071/RD21131. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2022. PMID: 35760398 Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of microRNAs and their target genes in oral submucous fibrosis.Oral Dis. 2023 Jul;29(5):1894-1904. doi: 10.1111/odi.14219. Epub 2022 May 3. Oral Dis. 2023. PMID: 35466497 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico and In Vitro Exploration of Poziotinib and Olmutinib Synergy in Lung Cancer: Role of hsa-miR-7-5p in Regulating Apoptotic Pathway Marker Genes.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 30;59(11):1923. doi: 10.3390/medicina59111923. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38003971 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and experimental validation to elucidate the pharmacological mechanisms of OATF against kidney stones.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 13;16:1575270. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1575270. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40432899 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the anti-breast cancer activity potential of east Kalimantan propolis by In vitro and bioinformatics analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 25;10(13):e33636. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33636. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wani T.A., Bakheit A.H., Zargar S., Khayyat A.I.A., Al-Majed A.A. Influence of Rutin, Sinapic Acid, and Naringenin on Binding of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Erlotinib to Bovine Serum Albumin Using Analytical Techniques Along with Computational Approach. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:3575. doi: 10.3390/app12073575. - DOI
-
- Zargar S., Alamery S., Bakheit A.H., Wani T.A. Poziotinib and bovine serum albumin binding characterization and influence of quercetin, rutin, naringenin and sinapic acid on their binding interaction. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020;235:118335. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118335. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wani T.A., Alanazi M.M., Alsaif N.A., Bakheit A.H., Zargar S., Alsalami O.M., Khan A.A. Interaction Characterization of a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Erlotinib with a Model Transport Protein in the Presence of Quercetin: A Drug–Protein and Drug–Drug Interaction Investigation Using Multi-Spectroscopic and Computational Approaches. Molecules. 2022;27:1265. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041265. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zargar S., Al-Majed A.R., Wani T.A. Potentiating and synergistic effect of grapefruit juice on the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of aripiprazole against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress in mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018;18:106. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2169-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lewandowska U., Gorlach S., Owczarek K., Hrabec E., Szewczyk K. Synergistic interactions between anticancer chemothera-peutics and phenolic compounds and anticancer synergy between polyphenols. Adv. Hyg. Exp. Med. 2014;68:528–540. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

