Connexin 43 Phosphorylation: Implications in Multiple Diseases
- PMID: 37446576
- PMCID: PMC10343229
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28134914
Connexin 43 Phosphorylation: Implications in Multiple Diseases
Abstract
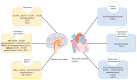
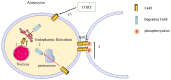
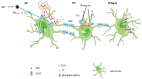
Connexin 43 (Cx43) is most widely distributed in mammals, especially in the cardiovascular and nervous systems. Its phosphorylation state has been found to be regulated by the action of more than ten kinases and phosphatases, including mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signaling and regulating kinase signaling. In addition, the phosphorylation status of different phosphorylation sites affects its own synthesis and assembly and the function of the gap junctions (GJs) to varying degrees. The phosphorylation of Cx43 can affect the permeability, electrical conductivity, and gating properties of GJs, thereby having various effects on intercellular communication and affecting physiological or pathological processes in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, clarifying the relationship between Cx43 phosphorylation and specific disease processes will help us better understand the disease. Based on the above clinical and preclinical findings, we present in this review the functional significance of Cx43 phosphorylation in multiple diseases and discuss the potential of Cx43 as a drug target in Cx43-related disease pathophysiology, with an emphasis on the importance of connexin 43 as an emerging therapeutic target in cardiac and neuroprotection.
Keywords: connexin 43; intercellular communication; phosphorylation; the cardiovascular system; the nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

