Evaluation of Antimicrobial, Anticholinesterase Potential of Indole Derivatives and Unexpectedly Synthesized Novel Benzodiazine: Characterization, DFT and Hirshfeld Charge Analysis
- PMID: 37446687
- PMCID: PMC10343724
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28135024
Evaluation of Antimicrobial, Anticholinesterase Potential of Indole Derivatives and Unexpectedly Synthesized Novel Benzodiazine: Characterization, DFT and Hirshfeld Charge Analysis
Abstract
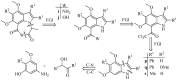
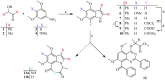
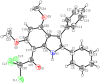
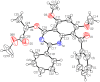
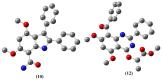
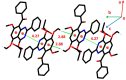
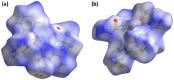
The pharmacological effectiveness of indoles, benzoxazepines and benzodiazepines initiated our synthesis of indole fused benoxazepine/benzodiazepine heterocycles, along with enhanced biological usefulness of the fused rings. Activated indoles 5, 6 and 7 were synthesized using modified Bischler indole synthesis rearrangement. Indole 5 was substituted with the trichloroacetyl group at the C7 position, yielding 8, exclusively due to the increased nucleophilic character of C7. When trichloroacylated indole 8 was treated with basified ethanol or excess amminia, indole acid 9 and amide 10 were yielded, respectively. Indole amide 10 was expected to give indole fused benoxazepine/benzodiazepine 11a/11b on treatment with alpha halo ester followed by a coupling agent, but when the reaction was tried, an unexpectedly rearranged novel product, 1,3-bezodiazine 12, was obtained. The synthetic compounds were screened for anticholinesterase and antibacterial potential; results showed all products to be very important candidates for both activities, and their potential can be explored further. In addition, 1,3-bezodiazine 12 was explored by DFT studies, Hirshfeld surface charge analysis and structural insight to obrain a good picture of the structure and reactivity of the products for the design of derivatised drugs from the novel compound.
Keywords: DFT; anticholinesterase; antimicrobial; benzodiazine; indole; novel benzodiazine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Modification of Bischler-Möhlau indole derivatives through palladium catalyzed Suzuki reaction as effective cholinesterase inhibitors, their kinetic and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Chem. 2018 Feb;76:166-176. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Bioorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29175588
-
Cyclohepta[b]indoles: A Privileged Structure Motif in Natural Products and Drug Design.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Nov 15;49(11):2390-2402. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00265. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27709885
-
Indol-2-Carboxylic Acid Esters Containing N-Phenylpiperazine Moiety - Preparation and Cholinesterase-inhibiting Activity.Curr Org Synth. 2020;17(7):576-587. doi: 10.2174/1570179417666200619132218. Curr Org Synth. 2020. PMID: 32560608
-
Medicinal Perspective of Indole Derivatives: Recent Developments and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(9):864-891. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666200310115327. Curr Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32156235 Review.
-
Indole Derivatives as Anti-Tubercular Agents: An Overview on their Synthesis and Biological Activities.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(22):4531-4568. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200918144709. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32951569 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Enzymatic and Computational Assessments of Pyrazole-Isatin and Pyrazole-Indole Conjugates as Anti-Diabetic, Anti-Arthritic, and Anti-Inflammatory Agents.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 23;17(3):293. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030293. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40142957 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the toxicological and beneficial effects of 4,5,6-Trimethoxy-2,3-diphenyl indole on Labeo rohita fingerlings.Sci Rep. 2025 May 9;15(1):16206. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01099-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40346157 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of dimeric 1,2-benzothiazine 1,1-dioxide scaffolds: molecular structures, Hirshfeld surface analysis, DFT and enzyme inhibition studies.RSC Adv. 2024 May 28;14(24):16935-16944. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02009j. eCollection 2024 May 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38808235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sachdeva H., Mathur J., Guleria A. Indole derivatives as potential anticancer agents: A review. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2020;65:4900–4907. doi: 10.4067/s0717-97072020000204900. - DOI
-
- Sayed M., Kamal El-Dean A.M., Ahmed M., Hassanien R. Design, synthesis, and characterization of novel pyrimidines bearing indole as antimicrobial agents. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2019;66:218–225. doi: 10.1002/jccs.201800115. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

