An AIE-Active NIR Fluorescent Probe with Good Water Solubility for the Detection of Aβ1-42 Aggregates in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 37446772
- PMCID: PMC10343367
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28135110
An AIE-Active NIR Fluorescent Probe with Good Water Solubility for the Detection of Aβ1-42 Aggregates in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
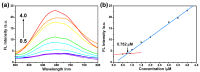
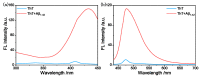
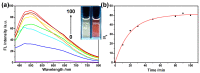
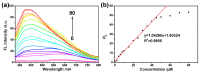
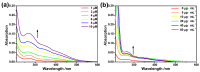
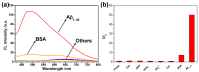
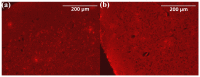
Alzheimer's disease (AD), an amyloid-related disease, seriously endangers the health of elderly individuals. According to current research, its main pathogenic factor is the amyloid protein, which is a kind of fibrillar aggregate formed by noncovalent self-assembly of proteins. Based on the characteristics of aggregation-induced emission (AIE), a bislactosyl-decorated tetraphenylethylene (TPE) molecule TMNL (TPE + malononitrile + lactose), bearing two malononitrile substituents, was designed and synthesized in this work. The amphiphilic TMNL could self-assemble into fluorescent organic nanoparticles (FONs) with near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence emission in physiological PBS (phosphate buffered saline), achieving excellent fluorescent enhancement (47-fold) upon its combination with Aβ1-42 fibrils. TMNL was successfully applied to image Aβ1-42 plaques in the brain tissue of AD transgenic mice, and due to the AIE properties of TMNL, no additional rinsing process was necessary. It is believed that the probe reported in this work should be useful for the sensitive detection and accurate localization mapping of Aβ1-42 aggregates related to Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: AIE; Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ; amyloid; fluorescence; lactose; near-infrared imaging; tetraphenylethylene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

